Influence of sex on outcomes of liver transplantation for hepatocellular carcinoma: a multicenter cohort study in China
- PMID: 38425217
- PMCID: PMC11033715
- DOI: 10.20892/j.issn.2095-3941.2023.0453
Influence of sex on outcomes of liver transplantation for hepatocellular carcinoma: a multicenter cohort study in China
Abstract
Objective: Sex-specific differences are observed in various liver diseases, but the influence of sex on the outcomes of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) after liver transplantation (LT) remains to be determined. This study is the first Chinese nationwide investigation of the role of sex in post-LT outcomes in patients with HCC.
Methods: Data for recipients with HCC registered in the China Liver Transplant Registry between January 2015 and December 2020 were analyzed. The associations between donor, recipient, or donor-recipient transplant patterns by sex and the post-LT outcomes were studied with propensity score matching (PSM). The survival associated with different sex-based donor-recipient transplant patterns was further studied.
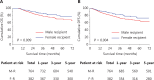
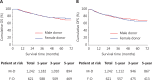
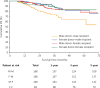
Results: Among 3,769 patients enrolled in this study, the 1-, 3-, and 5-year overall survival (OS) rates of patients with HCC after LT were 96.1%, 86.4%, and 78.5%, respectively, in female recipients, and 95.8%, 79.0%, and 70.7%, respectively, in male recipients after PSM (P = 0.009). However, the OS was comparable between recipients with female donors and male donors. Multivariate analysis indicated that male recipient sex was a risk factor for post-LT survival (HR = 1.381, P = 0.046). Among the donor-recipient transplant patterns, the male-male donor-recipient transplant pattern was associated with the poorest post-LT survival (P < 0.05).
Conclusions: Our findings highlighted that the post-LT outcomes of female recipients were significantly superior to those of male recipients, and the male-male donor-recipient transplant pattern was associated with the poorest post-LT survival. Livers from male donors may provide the most benefit to female recipients. Our results indicate that sex should be considered as a critical factor in organ allocation.
Keywords: Sex; donor; hepatocellular carcinoma; liver transplantation; outcome; recipient.
Copyright © 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflicts of interest are disclosed.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Recipient-Donor Sex Constellation in Liver Transplantation for Hepatocellular Carcinoma-An ELTR Study.Liver Int. 2025 Jan;45(1):e16178. doi: 10.1111/liv.16178. Epub 2024 Nov 20. Liver Int. 2025. PMID: 39564600 Free PMC article.
-
Donor factors similarly impact survival outcome after liver transplantation in hepatocellular carcinoma and non-hepatocellular carcinoma patients.Dig Dis Sci. 2014 Jan;59(1):214-9. doi: 10.1007/s10620-013-2883-7. Dig Dis Sci. 2014. PMID: 24077924
-
The Matching Status Between Donor and Recipient Hepatitis B Seroepidemiology Makes a Difference in Liver Transplantation for Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Clin Transl Gastroenterol. 2020 May;11(5):e00168. doi: 10.14309/ctg.0000000000000168. Clin Transl Gastroenterol. 2020. PMID: 32358239 Free PMC article.
-
Outcomes of Liver Transplantation Using Pediatric Deceased Donor Livers: A Single-Center Analysis of 102 Donors.Chin Med J (Engl). 2018 Mar 20;131(6):677-683. doi: 10.4103/0366-6999.226901. Chin Med J (Engl). 2018. PMID: 29521290 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Liver transplantation for cirrhosis and its complications.Acta Clin Belg. 2024 Oct;79(5):377-383. doi: 10.1080/17843286.2025.2456183. Epub 2025 Jan 21. Acta Clin Belg. 2024. PMID: 39834202 Review.
References
-
- Ling S, Jiang G, Que Q, Xu S, Chen J, Xu X. Liver transplantation in patients with liver failure: twenty years of experience from China. Liver Int. 2022;42:2110–6. - PubMed
-
- Briceño J, Calleja R, Hervás C. Artificial intelligence and liver transplantation: looking for the best donor-recipient pairing. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 2022;21:347–53. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- 2021YFA1100500/National Key Research and Development Program of China
- 92159202/The Major Research Plan of the National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 81930016/Key Program, National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82300743/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- LQ23H160044/Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
