Efficacy of the combination of myofunctional therapy (lip exercises) and activator high-pull headgear in the closure of interlabial gap in long-face skeletal class II patients with lip incompetence: A 6-8-month longitudinal randomized clinical trial
- PMID: 38425317
- PMCID: PMC10899158
Efficacy of the combination of myofunctional therapy (lip exercises) and activator high-pull headgear in the closure of interlabial gap in long-face skeletal class II patients with lip incompetence: A 6-8-month longitudinal randomized clinical trial
Abstract
Background: Lip incompetence is an important issue in orthodontics. No study has evaluated the effects of the combination of headgear + lip exercises on lip incompetence. Therefore, this study was conducted.
Materials and methods: This was a longitudinal randomized clinical trial on 29 subjects (16 controls and 13 experimental subjects). Both groups were treated with standardized activator high-pull headgear (and followed up monthly) for 6-8 months. In the experimental group, patients were also instructed to practice certain lip exercises 3 sessions a day, 5 times per session. Pre-/post-treatment interlabial gap, upper lip length and vermilion height, lower lip length and vermilion height, nasolabial angle, and profile convexity angle were measured clinically and photographically, immediately before treatment and after it. Data were analyzed using paired/unpaired t-tests (α = 0.025) and partial correlation coefficient controlling for the intervention type (α = 0.05).
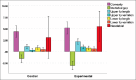
Results: Lip exercise plus activator headgear significantly changed/improved all parameters (P ≤ 0.006) over the 6-8-month course of treatment. Activator headgear alone changed/improved only 4 parameters: interlabial gap, upper and lower lip lengths, the lower lip vermilion height, and profile convexity (P ≤ 0.008). Compared to the control (activator headgear alone), in the experimental group, the changes observed in the interlabial gap closure (P = 0.011), upper lip lengthening (P = 0.002), and upper lip vermilion lengthening (P = 0.017) were significantly greater. Convexity angle corrections were more successful in cooperative patients (R = 0.469, P = 0.012). Cases with smaller pretreatment nasolabial angles may experience more changes in this angle after treatment (R = 0.581, P = 0.001).
Conclusion: The addition of lip exercises to activator high-pull headgear can boost activator headgear's efficacy in treating lip incompetence.
Keywords: Extraoral traction appliances; myofunctional therapy; orthodontics; randomized clinical trial.
Copyright: © 2024 Dental Research Journal.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors of this manuscript declare that they have no conflicts of interest, real or perceived, financial or nonfinancial in this article.
Figures
References
-
- Leonardo SE, Sato Y, Kaneko T, Yamamoto T, Handa K, Iida J. Differences in dento-facial morphology in lip competence and lip incompetence. Orthod Waves. 2009;68:12–9.
-
- Drevensek M, Stefanac-Papić J, Farcnik F. The influence of incompetent lip seal on the growth and development of craniofacial complex. Coll Antropol. 2005;29:429–34. - PubMed
-
- Wagaiyu EG, Ashley FP. Mouthbreathing, lip seal and upper lip coverage and their relationship with gingival inflammation in 11-14 year-old schoolchildren. J Clin Periodontol. 1991;18:698–702. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous