Upconverting photons at the molecular scale with lanthanide complexes
- PMID: 38425527
- PMCID: PMC10901487
- DOI: 10.1039/d3sc06099c
Upconverting photons at the molecular scale with lanthanide complexes
Abstract
In this perspective, we summarise the major milestones to date in the field of molecular upconversion (UC) with lanthanide based coordination complexes. This begins from the leap firstly from solid-state to nanoparticular regimes, and further down the scale to the molecular domain. We explain the mechanistic intricacies of each differing way of generating upconverted photons, critiquing them and outlining our views on the benefits and limitations of each process, also offering our perspective and opinion on where these new molecular UC edifices will take us. This nascent area is already rapidly expanding and improving, having increased in luminance efficiency by more than four orders of magnitude in the last decade: we conclude that the future is bright for molecular UC.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures



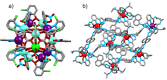


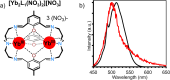




References
-
- Ramasamy P. Manivasakan P. Kim J. RSC Adv. 2014;4:34873. doi: 10.1039/C4RA03919J. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

