Identification of claudin-2 as a promising biomarker for early diagnosis of pre-diabetes
- PMID: 38425650
- PMCID: PMC10902111
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1370708
Identification of claudin-2 as a promising biomarker for early diagnosis of pre-diabetes
Abstract
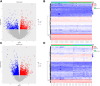
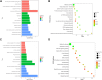
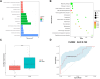
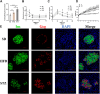
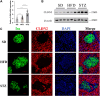
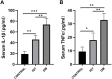
Introduction: Pre-diabetes, a high-risk metabolic state, is situated between normal glucose homeostasis and diabetes. Early identification of pre-diabetes offers opportunities for intervention and diabetes reversal, highlighting the crucial need to investigate reliable biomarkers for this condition. Methods: We conducted an in-depth bioinformatics analysis of clinical samples from non-diabetic (ND), impaired glucose tolerance (IGT), and type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) categories within the GSE164416 dataset. Thereafter the HFD and STZ treated mice were used for validation. Results: This analysis identified several codifferentially expressed genes (Co-DEGs) for IGT and T2DM, including CFB, TSHR, VNN2, APOC1, CLDN2, SLPI, LCN2, CXCL17, FAIM2, and REG3A. Validation of these genes and the determination of ROC curves were performed using the GSE76895 dataset. Thereafter, CLDN2 was selected for further verification. Gene expression analysis and immunofluorescence analysis revealed a significant upregulation of CLDN2 expression in the pancreas islets of mice in the high-fat diet and T2DM groups compared to the control group. Similarly, serum level of CLDN2 in patients with IGT and T2DM were significantly higher than those in the healthy group. Discussion: These results suggest that CLDN2 can serve as a novel biomarker for pre-diabetes, providing a new direction for future research in the prevention of type 2 diabetes.
Keywords: biomarker; claudin-2; diabetes; impaired glucose tolerance; pre diabetes.
Copyright © 2024 Songtao, Fangyu, Jie and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Identification of FGF13 as a Potential Biomarker and Target for Diagnosis of Impaired Glucose Tolerance.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jan 16;24(2):1807. doi: 10.3390/ijms24021807. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36675322 Free PMC article.
-
Surfactin Mitigates a High-Fat Diet and Streptozotocin-Induced Type 2 Diabetes through Improving Pancreatic Dysfunction and Inhibiting Inflammatory Response.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Sep 21;23(19):11086. doi: 10.3390/ijms231911086. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36232419 Free PMC article.
-
Lipocalin-2 expression and serum levels as early predictors of type 2 diabetes mellitus in obese women.IUBMB Life. 2017 Feb;69(2):88-97. doi: 10.1002/iub.1594. Epub 2017 Jan 24. IUBMB Life. 2017. PMID: 28116808
-
Platelet mean volume, distribution width, and count in type 2 diabetes, impaired fasting glucose, and metabolic syndrome: a meta-analysis.Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2015 May;31(4):402-10. doi: 10.1002/dmrr.2625. Epub 2014 Dec 29. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2015. PMID: 25421610 Review.
-
Impaired glucose tolerance and impaired fasting glucose--a review of diagnosis, clinical implications and management.Diab Vasc Dis Res. 2005 Feb;2(1):9-15. doi: 10.3132/dvdr.2005.007. Diab Vasc Dis Res. 2005. PMID: 16305067 Review.
Cited by
-
Expression and Targeted Application of Claudins Family in Hepatobiliary and Pancreatic Diseases.J Hepatocell Carcinoma. 2024 Sep 25;11:1801-1821. doi: 10.2147/JHC.S483861. eCollection 2024. J Hepatocell Carcinoma. 2024. PMID: 39345937 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

