Reliability of two devices for shoulder strength assessment: Wii Fit Balance Board and hand-held dynamometer
- PMID: 38425742
- PMCID: PMC10901178
- DOI: 10.1177/17585732221145558
Reliability of two devices for shoulder strength assessment: Wii Fit Balance Board and hand-held dynamometer
Abstract
Background: The aim of this study was to compare the reliability and agreement between two devices - Wii Fit Balance Board (WBB) versus Hand-Held Dynamometer (HHD) to measure isometric strength during the athletic shoulder (ASH) test in healthy amateur rugby players.
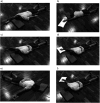
Methods: Fifteen males (23.73 ± 2.8 years) completed two testing sessions. Maximal isometric contractions using the dominant arm (D) and non-dominant arm (ND) against a WBB and HHD were assessed at three angles of abduction (180°, 'I'; 135°, 'Y' and 90°, 'T'), in a prone lying position.
Results: The results indicate a very large correlation between the HHD and the WBB. WBB provides acceptable reliability at I-Test D (CV = 9.97%, ICC = 0.88) and HHD in the I-Test D (CV = 8.90%, ICC = 0.94), I-Test ND (CV = 8.60%, ICC = 0.95) in peak strength values. The HHD is most reliable in D ASH I-Y-T (CV = 10.94%) and WBB (CV = 11.05%). In the ND ASH I-Y-T test, the HHD is the most reliable (CV = 12.5%) compared to the WBB (CV = 14.43%).
Conclusions: These results suggest that WBB is a reliable device to assess strength in the ASH test with a very large correlation with the HHD. WBB and HHD are two affordable devices to assess isometric shoulder strength.
Keywords: Reliability; isometric; shoulder; strength; upper extremity.
© The Author(s) 2022.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures



References
-
- Stark T, Walker B, Phillips JKet al. et al. Hand-held dynamometry correlation with the gold standard isokinetic dynamometry: a systematic review. PM R 2011; 3: 472–479. - PubMed
-
- Hopkins WG, Hawley JA, Burke LM. Design and analysis of research on sport performance enhancement. Med Sci Sports Exerc 1999; 31: 472–485. - PubMed
-
- Hopkins WG. Measures of reliability in sports medicine and science. Sports Med 2000; 30: 1–15. - PubMed
-
- Hopkins WG, Schabort EJ, Hawley JA. Reliability of power in physical performance tests. Sports Med 2001; 31: 211–234. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
