Asymmetrical Biantennary Glycans Prepared by a Stop-and-Go Strategy Reveal Receptor Binding Evolution of Human Influenza A Viruses
- PMID: 38425896
- PMCID: PMC10900492
- DOI: 10.1021/jacsau.3c00695
Asymmetrical Biantennary Glycans Prepared by a Stop-and-Go Strategy Reveal Receptor Binding Evolution of Human Influenza A Viruses
Abstract
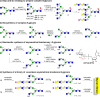
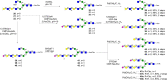
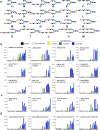
Glycan binding properties of respiratory viruses have been difficult to probe due to a lack of biologically relevant glycans for binding studies. Here, a stop-and-go chemoenzymatic methodology is presented that gave access to a panel of 32 asymmetrical biantennary N-glycans having various numbers of N-acetyl lactosamine (LacNAc) repeating units capped by α2,3- or α2,6-sialosides resembling structures found in airway tissues. It exploits that the branching enzymes MGAT1 and MGAT2 can utilize unnatural UDP-2-deoxy-2-trifluoro-N-acetamido-glucose (UDP-GlcNTFA) as donor. The TFA moiety of the resulting glycans can be hydrolyzed to give GlcNH2 at one of the antennae, which temporarily blocks extension by glycosyl transferases. The N-glycans were printed as a microarray that was probed for receptor binding specificities of the evolutionary distinct human A(H3N2) and A(H1N1)pdm09 viruses. It was found that not only the sialoside type but also the length of the LacNAc chain and presentation at the α1,3-antenna of N-glycans are critical for binding. Early A(H3N2) viruses bound to 2,6-sialosides at a single LacNAc moiety at the α1,3-antenna whereas later viruses required the sialoside to be presented at a tri-LacNAc moiety. Surprisingly, most of the A(H3N2) viruses that appeared after 2021 regained binding capacity to sialosides presented at a di-LacNAc moiety. As a result, these viruses again agglutinate erythrocytes, commonly employed for antigenic characterization of influenza viruses. Human A(H1N1)pdm09 viruses have similar receptor binding properties as recent A(H3N2) viruses. The data indicate that an asymmetric N-glycan having 2,6-sialoside at a di-LacNAc moiety is a commonly employed receptor by human influenza A viruses.
© 2024 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures

Update of
-
Asymmetrical Bi-antennary Glycans Prepared by a Stop-and-Go Strategy Reveal Receptor Binding Evolution of Human Influenza A Viruses.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Nov 9:2023.11.08.566285. doi: 10.1101/2023.11.08.566285. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: JACS Au. 2024 Jan 23;4(2):607-618. doi: 10.1021/jacsau.3c00695. PMID: 37986780 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- The top 10 causes of death. World Health Organization Newsroom, 2020, https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/the-top-10-causes-of-death.
-
- Walther T.; Karamanska R.; Chan R. W.; Chan M. C.; Jia N.; Air G.; Hopton C.; Wong M. P.; Dell A.; Malik Peiris J. S.; Haslam S. M.; Nicholls J. M. Glycomic analysis of human respiratory tract tissues and correlation with influenza virus infection. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e100322310.1371/journal.ppat.1003223. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
