Electrocatalytic Hydrogenation Using Palladium Membrane Reactors
- PMID: 38425903
- PMCID: PMC10900496
- DOI: 10.1021/jacsau.3c00647
Electrocatalytic Hydrogenation Using Palladium Membrane Reactors
Abstract
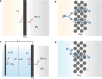
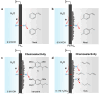
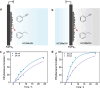
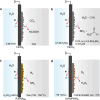
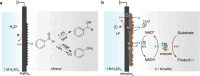
Hydrogenation is a crucial chemical process employed in a myriad of industries, often facilitated by metals such as Pd, Pt, and Ni as catalysts. Traditional thermocatalytic hydrogenation usually necessitates high temperature and elevated pressure, making the process energy intensive. Electrocatalytic hydrogenation offers an alternative but suffers from issues such as competing H2 evolution, electrolyte separation, and limited solvent selection. This Perspective introduces the evolution and advantages of the electrocatalytic Pd membrane reactor (ePMR) as a solution to these challenges. ePMR utilizes a Pd membrane to physically separate the electrochemical chamber from the hydrogenation chamber, permitting the use of water as the hydrogen source and eliminating the need for H2 gas. This setup allows for greater control over reaction conditions, such as solvent and electrolyte selection, while mitigating issues such as low Faradaic efficiency and complex product separation. Several representative hydrogenation reactions (e.g., hydrogenation of C=C, C≡C, C=O, C≡N, and O=O bonds) achieved via ePMR over the past 30 years were concisely discussed to highlight the unique advantages of ePMR. Promising research directions along with the advancement of ePMR for more challenging hydrogenation reactions are also proposed. Finally, we provide a prospect for future development of this distinctive hydrogenation strategy using hydrogen-permeable membrane electrodes.
© 2024 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Electricity-driven organic hydrogenation using water as the hydrogen source.Chem Sci. 2024 Sep 26;15(40):16424-35. doi: 10.1039/d4sc03836c. Online ahead of print. Chem Sci. 2024. PMID: 39371462 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Physical Separation of H2 Activation from Hydrogenation Chemistry Reveals the Specific Role of Secondary Metal Catalysts.Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2021 May 17;60(21):11937-11942. doi: 10.1002/anie.202017082. Epub 2021 Apr 14. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2021. PMID: 33851491
-
Designed Nanomaterials for Electrocatalytic Organic Hydrogenation Using Water as the Hydrogen Source.Acc Chem Res. 2023 Jul 4;56(13):1872-1883. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.3c00192. Epub 2023 Jun 14. Acc Chem Res. 2023. PMID: 37316974
-
Liquid Organic Hydrogen Carrier Concepts and Catalysts for Hydrogenation and Dehydrogenation Reactions.Molecules. 2024 Oct 18;29(20):4938. doi: 10.3390/molecules29204938. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 39459306 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Efficient Electrocatalytic Hydrogenation with a Palladium Membrane Reactor.J Am Chem Soc. 2019 May 15;141(19):7815-7821. doi: 10.1021/jacs.9b01442. Epub 2019 May 1. J Am Chem Soc. 2019. PMID: 30998338
Cited by
-
Experimental and theoretical validation for transmutation of palladium at electrochemical interfaces.Sci Rep. 2024 Sep 11;14(1):21270. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-70597-y. Sci Rep. 2024. Retraction in: Sci Rep. 2025 Aug 11;15(1):29359. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-15062-0. PMID: 39261516 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Electricity-driven organic hydrogenation using water as the hydrogen source.Chem Sci. 2024 Sep 26;15(40):16424-35. doi: 10.1039/d4sc03836c. Online ahead of print. Chem Sci. 2024. PMID: 39371462 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Accelerating lithium-mediated nitrogen reduction through an integrated palladium membrane hydrogenation reactor.Nat Commun. 2025 Jul 28;16(1):6696. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-62088-z. Nat Commun. 2025. PMID: 40721605 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nishimura S.Handbook of Heterogeneous Catalytic Hydrogenation for Organic Synthesis; Wiley: New York, 2001; p 63.
-
- Sheldon R. A.; van Bekkum H.. Fine Chemicals through Heterogeneous Catalysis; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, 2001; p 351.
-
- Sun Z.; Wang S.; Chen W. Metal Single-Atom Catalysts for Selective Hydrogenation of Unsaturated Bonds. J. Mater. Chem. A 2021, 9, 5296–5319. 10.1039/D1TA00022E. - DOI
-
- Diesen J. S.; Andersson P. G. Hydrogenation of Unfunctionalized Alkenes. In Modern Reduction Methods 2008, 39–64. 10.1002/9783527622115.ch2. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
