BACE1 Inhibition Utilizing Organic Compounds Holds Promise as a Potential Treatment for Alzheimer's and Parkinson's Diseases
- PMID: 38425997
- PMCID: PMC10904208
- DOI: 10.1155/2024/6654606
BACE1 Inhibition Utilizing Organic Compounds Holds Promise as a Potential Treatment for Alzheimer's and Parkinson's Diseases
Abstract
Background: Neurological disorders like Alzheimer's disease (AD) and Parkinson's disease (PD) manifest through gradually deteriorating cognitive functions. An encouraging strategy for addressing these disorders involves the inhibition of precursor-cleaving enzyme 1 (BACE1).
Objectives: In the current research, a virtual screening technique was employed to identify potential BACE1 inhibitors among selected herbal isolates.
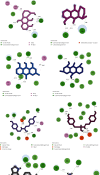
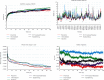
Methods: This study evaluated 79 flavonoids, anthraquinones (AQs), and cinnamic acid derivatives for their potential blood-brain barrier (BBB) permeability. Using the AutoDock 4.0 tool, molecular docking analysis was conducted to determine the binding affinity of BBB permeable compounds to the BACE1 active site. Molecular dynamics (MD) simulations were performed to assess the stability of the docked poses of the most potent inhibitors. The interactions between the most effective plant-based inhibitors and the residues within the BACE1 catalytic site were examined before and after MD simulations.
Results: Ponciretin, danthron, chrysophanol, and N-p-coumaroyltyramine were among the highest-ranking BACE1 inhibitors, with inhibition constant values calculated in the nanomolar range. Furthermore, during 10 ns simulations, the docked poses of these ligands were observed to be stable.
Conclusion: The findings propose that ponciretin, danthron, chrysophanol, and N-p-coumaroyltyramine might serve as potential choices for the treatment of AD and PD, laying the groundwork for the creation of innovative BACE1 inhibitors.
Copyright © 2024 Razieh Amini et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Virtual screening, ADMET prediction, molecular docking, and dynamic simulation studies of natural products as BACE1 inhibitors for the management of Alzheimer's disease.Sci Rep. 2024 Nov 2;14(1):26431. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-75292-6. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39488559 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibitory activities of major anthraquinones and other constituents from Cassia obtusifolia against β-secretase and cholinesterases.J Ethnopharmacol. 2016 Sep 15;191:152-160. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2016.06.037. Epub 2016 Jun 15. J Ethnopharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27321278
-
In-silico evaluations of the isolated phytosterols from polygonum hydropiper L against BACE1 and MAO drug targets.J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2022;40(20):10230-10238. doi: 10.1080/07391102.2021.1940286. Epub 2021 Jun 23. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2022. PMID: 34157942
-
Alzheimer's Disease and β-secretase Inhibition: An Update with a Focus on Computer-aided Inhibitor Design.Curr Drug Targets. 2022;23(3):266-285. doi: 10.2174/1389450122666210809100050. Curr Drug Targets. 2022. PMID: 34370634 Review.
-
Structure-Based Survey of the Binding Modes of BACE1 Inhibitors.ACS Chem Neurosci. 2019 Feb 20;10(2):880-889. doi: 10.1021/acschemneuro.8b00420. Epub 2018 Dec 27. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 30540177 Review.
Cited by
-
In silico drug repurposing at the cytoplasmic surface of human aquaporin 1.PLoS One. 2025 Jan 9;20(1):e0314151. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0314151. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 39787482 Free PMC article.
-
Exploration of small molecules as inhibitors of potential BACE1 protein to treat amyloid cerebrovascular disease by employing molecular modeling and simulation approaches.PLoS One. 2025 Mar 21;20(3):e0317716. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0317716. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40117242 Free PMC article.
-
New Insights into the Development of Donepezil-Based Hybrid and Natural Molecules as Multi-Target Drug Agents for Alzheimer's Disease Treatment.Molecules. 2024 Nov 11;29(22):5314. doi: 10.3390/molecules29225314. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 39598703 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Flavonoids as Promising Akt1 Inhibitors in Cancer Medicine: Insights From Molecular Docking, Dynamics, DFT Calculations, and In Vitro Validation.Cancer Rep (Hoboken). 2025 Aug;8(8):e70315. doi: 10.1002/cnr2.70315. Cancer Rep (Hoboken). 2025. PMID: 40798865 Free PMC article.
-
Cinnamic Acid Derivatives: Recent Discoveries and Development Strategies for Alzheimer's Disease.Mini Rev Med Chem. 2025;25(2):163-175. doi: 10.2174/0113895575330648240819112435. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2025. PMID: 39219429 Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

