Facile synthesis of nanoparticles-stacked Co3O4 nanoflakes with catalase-like activity for accelerating wound healing
- PMID: 38426010
- PMCID: PMC10902680
- DOI: 10.1093/rb/rbae006
Facile synthesis of nanoparticles-stacked Co3O4 nanoflakes with catalase-like activity for accelerating wound healing
Abstract
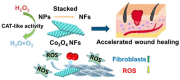
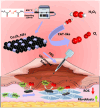
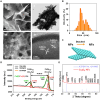
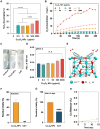
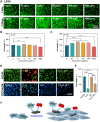
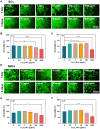
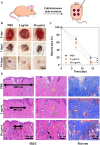
Delayed wound healing caused by excessive reactive oxygen species (ROS) remains a considerable challenge. In recent years, metal oxide nanozymes have gained significant attention in biomedical research. However, a comprehensive investigation of Co3O4-based nanozymes for enhancing wound healing and tissue regeneration is lacking. This study focuses on developing a facile synthesis method to produce high-stability and cost-effective Co3O4 nanoflakes (NFs) with promising catalase (CAT)-like activity to regulate the oxidative microenvironment and accelerate wound healing. The closely arranged Co3O4 nanoparticles (NPs) within the NFs structure result in a significantly larger surface area, thereby amplifying the enzymatic activity compared to commercially available Co3O4 NPs. Under physiological conditions, it was observed that Co3O4 NFs efficiently break down hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) without generating harmful radicals (·OH). Moreover, they exhibit excellent compatibility with various cells involved in wound healing, promoting fibroblast growth and protecting cells from oxidative stress. In a rat model, Co3O4 NFs facilitate both the hemostatic and proliferative phases of wound healing, consequently accelerating the process. Overall, the promising results of Co3O4 NFs highlight their potential in promoting wound healing and tissue regeneration.
Keywords: Co3O4; nanoflake; nanozyme; reactive oxygen species; wound healing.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press.
Figures
References
-
- Zhao Y, Song S, Ren X, Zhang J, Lin Q, Zhao Y.. Supramolecular adhesive hydrogels for tissue engineering applications. Chem Rev 2022;122:5604–40. - PubMed
-
- Rodriguez PG, Felix FN, Woodley DT, Shim EK.. The role of oxygen in wound healing: a review of the literature. Dermatol Surg 2008;34:1159–69. - PubMed
-
- Zhang H, Zhang W, Qiu H, Zhang G, Li X, Qi H, Guo J, Qian J, Shi X, Gao X, Shi D, Zhang D, Gao R, Ding J.. A biodegradable metal-polymer composite stent safe and effective on physiological and serum-containing biomimetic conditions. Adv Healthc Mater 2022;11:e2201740. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

