What can we learn from treatments of oral lichen planus?
- PMID: 38426013
- PMCID: PMC10902003
- DOI: 10.3389/fcimb.2024.1279220
What can we learn from treatments of oral lichen planus?
Abstract
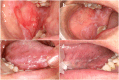
Oral lichen planus (OLP), a T-lymphocyte-mediated disease of the oral mucosa, has a complex pathogenesis that involves a number of factors. The disease is characterized by recurrent episodes and requires continuous follow up, and there is no curative treatment available. Erosive lichen planus, among others, has a risk of malignant transformation and requires standardized treatment to control its progression. Different clinical subtypes of oral lichen planus require appropriate treatment. Pharmacological treatments are the most widely available and have the greatest variety of options and a number of novel pharmacological treatments are presented as highlights, including JAK enzyme inhibitors. The second is photodynamic therapy, which is the leading physiological treatment. In addition, periodontal treatment and psychological treatment should not be neglected. In this review, we briefly discuss the most recent developments in therapies for oral lichen planus after summarizing the most widely used clinical treatments, aiming to provide different proposals for future clinical treatment.
Keywords: erosive type; microbes; nonpharmacological treatment; oral lichen planus; pharmacological treatment.
Copyright © 2024 Wu, Bai, Jing and Chen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Evaluation of Potential Risk Factors that contribute to Malignant Transformation of Oral Lichen Planus: A Literature Review.J Contemp Dent Pract. 2016 Aug 1;17(8):692-701. doi: 10.5005/jp-journals-10024-1914. J Contemp Dent Pract. 2016. PMID: 27659090 Review.
-
Photodynamic therapy for refractory erosive oral lichen planus: a case series study.Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol. 2024 Mar;137(3):e41-e44. doi: 10.1016/j.oooo.2023.11.013. Epub 2023 Dec 5. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol. 2024. PMID: 38278673
-
Oral lichen planus part II: therapy and malignant transformation.Skinmed. 2004 Jan-Feb;3(1):19-22. doi: 10.1111/j.1540-9740.2004.02523.x. Skinmed. 2004. PMID: 14724408 Review.
-
Oral lichen planus: a review.Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2000 Aug;38(4):370-7. doi: 10.1054/bjom.2000.0335. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2000. PMID: 10922170 Review.
-
A clinical study of 674 patients with oral lichen planus in China.J Oral Pathol Med. 2005 Sep;34(8):467-72. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0714.2005.00341.x. J Oral Pathol Med. 2005. PMID: 16091113
Cited by
-
The role of skin microbiota in lichen planus from a Mendelian randomization perspective.Arch Dermatol Res. 2025 Jan 15;317(1):245. doi: 10.1007/s00403-024-03677-8. Arch Dermatol Res. 2025. PMID: 39812683
-
Efficacy of Combined vs. Monotherapy in Oral Lichen Planus: A Randomized Clinical Trial.Oral Dis. 2025 Feb;31(2):522-531. doi: 10.1111/odi.15151. Epub 2024 Oct 22. Oral Dis. 2025. PMID: 39435599 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Erosive oral lichen planus successfully treated with JAK3/TEC inhibitor ritlecitinib: A case report.JAAD Case Rep. 2025 Jun 16;63:70-72. doi: 10.1016/j.jdcr.2025.05.017. eCollection 2025 Sep. JAAD Case Rep. 2025. PMID: 40787044 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Animal models to study the pathogenesis and novel therapeutics of oral lichen planus.Front Oral Health. 2024 May 9;5:1405245. doi: 10.3389/froh.2024.1405245. eCollection 2024. Front Oral Health. 2024. PMID: 38783985 Free PMC article.
-
Translational Research in Oral Lichen Planus: From Laboratory Discoveries to Clinical Applications.Cureus. 2024 Oct 14;16(10):e71462. doi: 10.7759/cureus.71462. eCollection 2024 Oct. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39544604 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

