Multi-omics analysis of miRNA-mediated intestinal microflora changes in crucian carp Carassius auratus infected with Rahnella aquatilis
- PMID: 38426108
- PMCID: PMC10902443
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1335602
Multi-omics analysis of miRNA-mediated intestinal microflora changes in crucian carp Carassius auratus infected with Rahnella aquatilis
Abstract
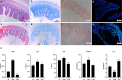
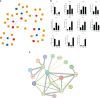
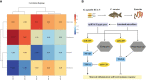
Infection by an emerging bacterial pathogen Rahnella aquatilis caused enteritis and septicemia in fish. However, the molecular pathogenesis of enteritis induced by R. aquatilis infection and its interacting mechanism of the intestinal microflora associated with microRNA (miRNA) immune regulation in crucian carp Carassius auratus are still unclear. In this study, C. auratus intraperitoneally injected with R. aquatilis KCL-5 was used as an experimental animal model, and the intestinal pathological changes, microflora, and differentially expressed miRNAs (DEMs) were investigated by multi-omics analysis. The significant changes in histopathological features, apoptotic cells, and enzyme activities (e.g., lysozyme (LYS), alkaline phosphatase (AKP), alanine aminotransferase (ALT), aspartate transaminase (AST), and glutathione peroxidase (GSH-Px)) in the intestine were examined after infection. Diversity and composition analysis of the intestinal microflora clearly demonstrated four dominant bacteria: Proteobacteria, Fusobacteria, Bacteroidetes, and Firmicutes. A total of 87 DEMs were significantly screened, and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) enrichment analyses revealed that the potential target genes were mainly involved in the regulation of lipid, glutathione, cytosine, and purine metabolism, which participated in the local immune response through the intestinal immune network for IgA production, lysosome, and Toll-like receptor (TLR) pathways. Moreover, the expression levels of 11 target genes (e.g., TLR3, MyD88, NF-κB, TGF-β, TNF-α, MHC II, IL-22, LysC, F2, F5, and C3) related to inflammation and immunity were verified by qRT-PCR detection. The correlation analysis indicated that the abundance of intestinal Firmicutes and Proteobacteria was significantly associated with the high local expression of miR-203/NF-κB, miR-129/TNF-α, and miR-205/TGF-β. These findings will help to elucidate the molecular regulation mechanism of the intestinal microflora, inflammation, and immune response-mediated miRNA-target gene axis in cyprinid fish.
Keywords: Carassius auratus; Rahnella aquatilis; inflammation; intestinal microflora; miRNA.
Copyright © 2024 Huo, Li, Hu and Lv.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Alteration of Immune Function and Gut Microbiome Composition in Carassius auratus Challenged With Rahnella aquatilis.J Fish Dis. 2025 Mar;48(3):e14054. doi: 10.1111/jfd.14054. Epub 2024 Dec 3. J Fish Dis. 2025. PMID: 39624934
-
Multiomics analysis revealed miRNAs as potential regulators of the immune response in Carassius auratus gills to Aeromonas hydrophila infection.Front Immunol. 2023 Feb 3;14:1098455. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1098455. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36820086 Free PMC article.
-
Ginger polysaccharide alleviates the effects of acute exposure to carbonate in crucian carp (Carassius auratus) by regulating immunity, intestinal microbiota, and intestinal metabolism.Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2024 Mar 15;273:116127. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2024.116127. Epub 2024 Feb 22. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2024. PMID: 38394756
-
Regulation of the MIR155 host gene in physiological and pathological processes.Gene. 2013 Dec 10;532(1):1-12. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2012.12.009. Epub 2012 Dec 14. Gene. 2013. PMID: 23246696 Review.
-
Genetic and Epigenetic Regulation of the Innate Immune Response to Gout.Immunol Invest. 2023 Apr;52(3):364-397. doi: 10.1080/08820139.2023.2168554. Epub 2023 Feb 6. Immunol Invest. 2023. PMID: 36745138 Review.
References
-
- Huang M, Wei X, Wu T, Li M, Zhou L, Chai L, et al. . Inhibition of TNBS-induced intestinal inflammation in crucian carp (Carassius carassius) by oral administration of bioactive Bioactive food derived peptides. Fish Shellfish Immunol (2022) 131:999–1005. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2022.09.044 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

