Genome-wide association studies reveal stable loci for wheat grain size under different sowing dates
- PMID: 38426132
- PMCID: PMC10903348
- DOI: 10.7717/peerj.16984
Genome-wide association studies reveal stable loci for wheat grain size under different sowing dates
Abstract
Background: Wheat (Tritium aestivum L.) production is critical for global food security. In recent years, due to climate change and the prolonged growing period of rice varieties, the delayed sowing of wheat has resulted in a loss of grain yield in the area of the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River. It is of great significance to screen for natural germplasm resources of wheat that are resistant to late sowing and to explore genetic loci that stably control grain size and yield.
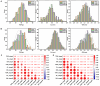
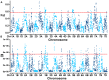
Methods: A collection of 327 wheat accessions from diverse sources were subjected to genome-wide association studies using genotyping-by-sequencing. Field trials were conducted under normal, delayed, and seriously delayed sowing conditions for grain length, width, and thousand-grain weight at two sites. Additionally, the additive main effects and multiplicative interaction (AMMI) model was applied to evaluate the stability of thousand-grain weight of 327 accessions across multiple sowing dates.
Results: Four wheat germplasm resources have been screened, demonstrating higher stability of thousand-grain weight. A total of 43, 35, and 39 significant MTAs were determined across all chromosomes except for 4D under the three sowing dates, respectively. A total of 10.31% of MTAs that stably affect wheat grain size could be repeatedly identified in at least two sowing dates, with PVE ranging from 0.03% to 38.06%. Among these, six were for GL, three for GW, and one for TGW. There were three novel and stable loci (4A_598189950, 4B_307707920, 2D_622241054) located in conserved regions of the genome, which provide excellent genetic resources for pyramid breeding strategies of superior loci. Our findings offer a theoretical basis for cultivar improvement and marker-assisted selection in wheat breeding practices.
Keywords: Breeding; Genome-wide association study; Grain size; Sowing dates; Stability; Wheat.
©2024 Hong et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare there are no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Genome-wide association study identifies QTL for thousand grain weight in winter wheat under normal- and late-sown stressed environments.Theor Appl Genet. 2021 Jan;134(1):143-157. doi: 10.1007/s00122-020-03687-w. Epub 2020 Oct 8. Theor Appl Genet. 2021. PMID: 33030571
-
Graphical analysis of multi-environmental trials for wheat grain yield based on GGE-biplot analysis under diverse sowing dates.BMC Plant Biol. 2023 Apr 17;23(1):198. doi: 10.1186/s12870-023-04197-9. BMC Plant Biol. 2023. PMID: 37062826 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide association study of six quality-related traits in common wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) under two sowing conditions.Theor Appl Genet. 2021 Jan;134(1):399-418. doi: 10.1007/s00122-020-03704-y. Epub 2020 Nov 5. Theor Appl Genet. 2021. PMID: 33155062
-
Genetic dissection of quantitative trait loci for grain size and weight by high-resolution genetic mapping in bread wheat (Triticum aestivum L.).Theor Appl Genet. 2022 Jan;135(1):257-271. doi: 10.1007/s00122-021-03964-2. Epub 2021 Oct 13. Theor Appl Genet. 2022. PMID: 34647130
-
Deciphering spike architecture formation towards yield improvement in wheat.J Genet Genomics. 2023 Nov;50(11):835-845. doi: 10.1016/j.jgg.2023.02.015. Epub 2023 Mar 11. J Genet Genomics. 2023. PMID: 36907353 Review.
Cited by
-
Survey and Identification of Fusarium Head Blight Pathogens of Wheat in the Western Cape Region of South Africa.Pathogens. 2025 Jan 16;14(1):80. doi: 10.3390/pathogens14010080. Pathogens. 2025. PMID: 39861041 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Basheir SMO, Hong Y, Lv C, Xu H, Zhu J, Guo B, Wang F, Xu R. Identification of wheat germplasm resistance to late sowing. Agronomy. 2023;13:1010. doi: 10.3390/agronomy13041010. - DOI
-
- Bates D, Mächler M, Bolker B, Walker S. Fitting linear mixed-effects models using lme4. Journal of Statistical Software. 2015;67(1):1–48. doi: 10.18637/jss.v067.i01. - DOI
-
- Chai S, Yao Q, Liu R, Xiang W, Xiao X, Fan X, Zeng J, Sha L, Kang H, Zhang H, Long D, Wu D, Zhou Y, Wang Y. Identification and validation of a major gene for kernel length at the P1 locus in Triticum polonicum. The Crop Journal. 2022;10:387–396. doi: 10.1016/j.cj.2021.07.006. - DOI
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

