Exploring miRNA‑target gene profiles associated with drug resistance in patients with breast cancer receiving neoadjuvant chemotherapy
- PMID: 38426156
- PMCID: PMC10902752
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2024.14291
Exploring miRNA‑target gene profiles associated with drug resistance in patients with breast cancer receiving neoadjuvant chemotherapy
Abstract
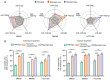
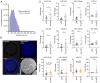
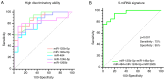
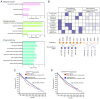
Exosomal microRNAs (miRNAs) are closely related to drug resistance in patients with breast cancer (BC); however, only a few roles of the exosomal miRNA-target gene networks have been clinically implicated in drug resistance in BC. Therefore, the present study aimed to identify the differential expression of exosomal miRNAs associated with drug resistance and their target mRNAs. In vitro microarray analysis was used to verify differentially expressed miRNAs (DEMs) in drug-resistant BC. Next, tumor-derived exosomes (TDEs) were isolated. Furthermore, it was determined whether the candidate drug-resistant miRNAs were also significant in TDEs, and then putative miRNAs in TDEs were validated in plasma samples from 35 patients with BC (20 patients with BC showing no response and 15 patients with BC showing a complete response). It was confirmed that the combination of five exosomal miRNAs, including miR-125b-5p, miR-146a-5p, miR-484, miR-1246-5p and miR-1260b, was effective for predicting therapeutic response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy, with an area under the curve value of 0.95, sensitivity of 75%, and specificity of 95%. Public datasets were analyzed to identify differentially expressed genes (DEGs) related to drug resistance and it was revealed that BAK1, NOVA1, PTGER4, RTKN2, AGO1, CAP1, and ETS1 were the target genes of exosomal miRNAs. Networks between DEMs and DEGs were highly correlated with mitosis, metabolism, drug transport, and immune responses. Consequently, these targets could be used as predictive markers and therapeutic targets for clinical applications to enhance treatment outcomes for patients with BC.
Keywords: breast cancer; drug resistance; exosomes; gene profile; miRNA; neoadjuvant chemotherapy.
Copyright: © Kim et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Identification of exosomal miR-455-5p and miR-1255a as therapeutic targets for breast cancer.Biosci Rep. 2020 Jan 31;40(1):BSR20190303. doi: 10.1042/BSR20190303. Biosci Rep. 2020. PMID: 31763681 Free PMC article.
-
Cisplatin-resistant MDA-MB-231 Cell-derived Exosomes Increase the Resistance of Recipient Cells in an Exosomal miR-423-5p-dependent Manner.Curr Drug Metab. 2019;20(10):804-814. doi: 10.2174/1389200220666190819151946. Curr Drug Metab. 2019. PMID: 31424364
-
Exosomes from tamoxifen-resistant breast cancer cells transmit drug resistance partly by delivering miR-9-5p.Cancer Cell Int. 2021 Jan 15;21(1):55. doi: 10.1186/s12935-020-01659-0. Cancer Cell Int. 2021. PMID: 33451320 Free PMC article.
-
Predictive miRNAs Patterns in Blood of Breast Cancer Patients Demonstrating Resistance Towards Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy.Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press). 2023 Aug 11;15:591-604. doi: 10.2147/BCTT.S415080. eCollection 2023. Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press). 2023. PMID: 37593370 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging roles of exosomal miRNAs in breast cancer drug resistance.IUBMB Life. 2019 Nov;71(11):1672-1684. doi: 10.1002/iub.2116. Epub 2019 Jul 19. IUBMB Life. 2019. PMID: 31322822 Review.
Cited by
-
Tumor-derived EV miRNA signatures surpass total EV miRNA in supplementing mammography for precision breast cancer diagnosis.Theranostics. 2024 Oct 7;14(17):6587-6604. doi: 10.7150/thno.99245. eCollection 2024. Theranostics. 2024. PMID: 39479442 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Spring LM, Fell G, Arfe A, Sharma C, Greenup R, Reynolds KL, Smith BL, Alexander B, Moy B, Isakoff SJ, et al. Pathologic complete response after neoadjuvant chemotherapy and impact on breast cancer recurrence and survival: A comprehensive meta-analysis. Clin Cancer Res. 2020;26:2838–2848. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-19-3492. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Echeverria GV, Ge Z, Seth S, Seth S, Zhang X, Jeter-Jones S, Zhou X, Cai S, Tu Y, McCoy A, et al. Resistance to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in triple-negative breast cancer mediated by a reversible drug-tolerant state. Sci Transl Med. 2019;11:eaav0936. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aav0936. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hoogstraat M, Lips EH, Mayayo-Peralta I, Mulder L, Kristel P, van der Heijden I, Annunziato S, van Seijen M, Nederlof PM, Sonke GS, et al. Comprehensive characterization of pre- and post-treatment samples of breast cancer reveal potential mechanisms of chemotherapy resistance. NPJ Breast Cancer. 2022;8:60. doi: 10.1038/s41523-022-00428-8. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lips EH, Michaut M, Hoogstraat M, Mulder L, Besselink NJ, Koudijs MJ, Cuppen E, Voest EE, Bernards R, Nederlof PM, et al. Next generation sequencing of triple negative breast cancer to find predictors for chemotherapy response. Breast Cancer Res. 2015;17:134. doi: 10.1186/s13058-015-0642-8. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
