Quantitative double echo steady state T2 mapping of upper extremity peripheral nerves and muscles
- PMID: 38426170
- PMCID: PMC10902120
- DOI: 10.3389/fneur.2024.1359033
Quantitative double echo steady state T2 mapping of upper extremity peripheral nerves and muscles
Abstract
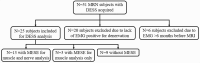
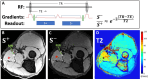
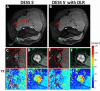
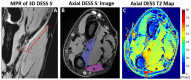
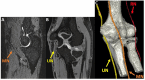
Introduction: T2 mapping can characterize peripheral neuropathy and muscle denervation due to axonal damage. Three-dimensional double echo steady-state (DESS) can simultaneously provide 3D qualitative information and T2 maps with equivalent spatial resolution. However, insufficient signal-to-noise ratio may bias DESS-T2 values. Deep learning reconstruction (DLR) techniques can reduce noise, and hence may improve quantitation of high-resolution DESS-T2. This study aims to (i) evaluate the effect of DLR methods on DESS-T2 values, and (ii) to evaluate the feasibility of using DESS-T2 maps to differentiate abnormal from normal nerves and muscles in the upper extremities, with abnormality as determined by electromyography.
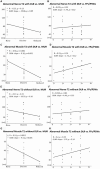
Methods and results: Analysis of images from 25 subjects found that DLR decreased DESS-T2 values in abnormal muscles (DLR = 37.71 ± 9.11 msec, standard reconstruction = 38.56 ± 9.44 msec, p = 0.005) and normal muscles (DLR: 27.18 ± 6.34 msec, standard reconstruction: 27.58 ± 6.34 msec, p < 0.001) consistent with a noise reduction bias. Mean DESS-T2, both with and without DLR, was higher in abnormal nerves (abnormal = 75.99 ± 38.21 msec, normal = 35.10 ± 9.78 msec, p < 0.001) and muscles (abnormal = 37.71 ± 9.11 msec, normal = 27.18 ± 6.34 msec, p < 0.001). A higher DESS-T2 in muscle was associated with electromyography motor unit recruitment (p < 0.001).
Discussion: These results suggest that quantitative DESS-T2 is improved by DLR and can differentiate the nerves and muscles involved in peripheral neuropathies from those uninvolved.
Keywords: T2 mapping; deep learning reconstruction; magnetic resonance neurography; peripheral neuropathy; quantitative MRI.
Copyright © 2024 Campbell, Sneag, Queler, Lin, Li and Tan.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Rapid quantitative T2 mapping of the prostate using three-dimensional dual echo steady state MRI at 3T.Magn Reson Med. 2016 Dec;76(6):1720-1729. doi: 10.1002/mrm.26053. Epub 2016 Jan 13. Magn Reson Med. 2016. PMID: 26765746
-
Quantitative MRI Differentiates Electromyography Severity Grades of Denervated Muscle in Neuropathy of the Brachial Plexus.J Magn Reson Imaging. 2022 Oct;56(4):1104-1115. doi: 10.1002/jmri.28125. Epub 2022 Feb 23. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2022. PMID: 35195321 Free PMC article.
-
Utility of accelerated T2-weighted turbo spin-echo imaging with deep learning reconstruction in female pelvic MRI: a multi-reader study.Eur Radiol. 2023 Nov;33(11):7697-7706. doi: 10.1007/s00330-023-09781-z. Epub 2023 Jun 14. Eur Radiol. 2023. PMID: 37314472
-
3D MR Neurography of craniocervical nerves: comparing DESS and post-contrast STIR with deeplearning-based reconstruction at 1.5T.AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2025 Mar 26:ajnr.A8750. doi: 10.3174/ajnr.A8750. Online ahead of print. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2025. PMID: 40139904
-
T2 Relaxation Times at Cardiac MRI in Healthy Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Radiology. 2020 Nov;297(2):344-351. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2020200989. Epub 2020 Aug 25. Radiology. 2020. PMID: 32840469 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Use of Magnetic Resonance Neurography for Sensory Nerve Injuries of the Head and Neck.Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2025 Jan 27;13(1):e6475. doi: 10.1097/GOX.0000000000006475. eCollection 2025 Jan. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2025. PMID: 39872082 Free PMC article.
-
Deep learning-based acceleration of muscle water T2 mapping in patients with neuromuscular diseases by more than 50% - translating quantitative MRI from research to clinical routine.PLoS One. 2025 Apr 16;20(4):e0318599. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0318599. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40238781 Free PMC article.
-
Magnetic Resonance Imaging of the Peripheral Nerves and Fascicles of the Knee Using Double Echo Steady State Sequence at 7 Tesla.Korean J Radiol. 2025 Jun;26(6):581-592. doi: 10.3348/kjr.2024.0912. Korean J Radiol. 2025. PMID: 40432262 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

