m6A methyltransferase METTL14‑mediated RP1‑228H13.5 promotes the occurrence of liver cancer by targeting hsa‑miR‑205/ZIK1
- PMID: 38426536
- PMCID: PMC10926101
- DOI: 10.3892/or.2024.8718
m6A methyltransferase METTL14‑mediated RP1‑228H13.5 promotes the occurrence of liver cancer by targeting hsa‑miR‑205/ZIK1
Abstract
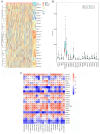
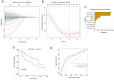
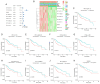
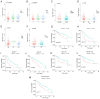
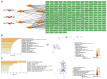
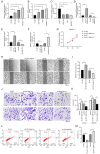
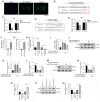
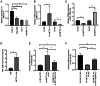
The aim of the present study was to explore the association between N6‑methyladenosine (m6A) modification regulatory gene‑related long noncoding (lnc)RNA RP1‑228H13.5 and cancer prognosis through bioinformatics analysis, as well as the impact of RP1‑228H13.5 on cell biology‑related behaviors and specific molecular mechanisms. Bioinformatics analysis was used to construct a risk model consisting of nine genes. This model can reflect the survival time and differentiation degree of cancer. Subsequently, a competing endogenous RNA network consisting of 3 m6A‑related lncRNAs, six microRNAs (miRs) and 201 mRNAs was constructed. A cell assay confirmed that RP1‑228H13.5 is significantly upregulated in liver cancer cells, which can promote liver cancer cell proliferation, migration and invasion, and inhibit liver cancer cell apoptosis. The specific molecular mechanism may be the regulation of the expression of zinc finger protein interacting with K protein 1 (ZIK1) by targeting the downstream hsa‑miR‑205. Further experiments found that the m6A methyltransferase 14, N6‑adenosine‑methyltransferase subunit mediates the regulation of miR‑205‑5p expression by RP1‑228H13.5. m6A methylation regulatory factor‑related lncRNA has an important role in cancer. The targeting of hsa‑miR‑205 by RP1‑228H13.5 to regulate ZIK1 may serve as a potential mechanism in the occurrence and development of liver cancer.
Keywords: METTL14; RP1-228H13.5/hsa‑miR‑205/ZIK1; lncRNA; m6A methylated.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Long noncoding RNA lnc-H2AFV-1 promotes cell growth by regulating aberrant m6A RNA modification in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.Cancer Sci. 2022 Jun;113(6):2071-2084. doi: 10.1111/cas.15366. Epub 2022 Apr 22. Cancer Sci. 2022. PMID: 35403343 Free PMC article.
-
[Study on the Role and Mechanism of METTL3 Mediating the Up-regulation of m6A Modified Long Non-coding RNA THAP7-AS1 in Promoting the Occurrence of Lung Cancer].Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2024 Jan 2;26(12):919-933. doi: 10.3779/j.issn.1009-3419.2023.102.45. Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2024. PMID: 38163978 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
METTL14 suppresses proliferation and metastasis of colorectal cancer by down-regulating oncogenic long non-coding RNA XIST.Mol Cancer. 2020 Feb 28;19(1):46. doi: 10.1186/s12943-020-1146-4. Mol Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32111213 Free PMC article.
-
Interaction between m6A and ncRNAs and Its Association with Diseases.Cytogenet Genome Res. 2022;162(4):171-187. doi: 10.1159/000526035. Epub 2022 Sep 19. Cytogenet Genome Res. 2022. PMID: 36122561 Review.
-
METTL14‑mediated RNA methylation in digestive system tumors.Int J Mol Med. 2023 Sep;52(3):86. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2023.5289. Epub 2023 Aug 4. Int J Mol Med. 2023. PMID: 37539726 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Targeting m6A RNA Modification in Tumor Therapeutics.Curr Oncol. 2025 Mar 11;32(3):159. doi: 10.3390/curroncol32030159. Curr Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40136363 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

