Targeting mitochondrial bioenergetics by combination treatment with imatinib and dichloroacetate in human erythroleukemic K‑562 and colorectal HCT‑116 cancer cells
- PMID: 38426621
- PMCID: PMC10919756
- DOI: 10.3892/ijo.2024.5630
Targeting mitochondrial bioenergetics by combination treatment with imatinib and dichloroacetate in human erythroleukemic K‑562 and colorectal HCT‑116 cancer cells
Abstract
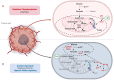
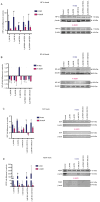
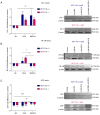
Tumor malignant cells are characterized by dysregulation of mitochondrial bioenergetics due to the 'Warburg effect'. In the present study, this metabolic imbalance was explored as a potential target for novel cancer chemotherapy. Imatinib (IM) downregulates the expression levels of SCΟ2 and FRATAXIN (FXN) genes involved in the heme‑dependent cytochrome c oxidase biosynthesis and assembly pathway in human erythroleukemic IM‑sensitive K‑562 chronic myeloid leukemia cells (K‑562). In the present study, it was investigated whether the treatment of cancer cells with IM (an inhibitor of oxidative phosphorylation) separately, or together with dichloroacetate (DCA) (an inhibitor of glycolysis), can inhibit cell proliferation or cause death. Human K‑562 and IM‑chemoresistant K‑562 chronic myeloid leukemia cells (K‑562R), as well as human colorectal carcinoma cells HCT‑116 (+/+p53) and (‑/‑p53, with double TP53 knock-in disruptions), were employed. Treatments of these cells with either IM (1 or 2 µM) and/or DCA (4 mΜ) were also assessed for the levels of several process biomarkers including SCO2, FXN, lactate dehydrogenase A, glyceraldehyde‑3‑phosphate dehydrogenase, pyruvate kinase M2, hypoxia inducing factor‑1a, heme oxygenase‑1, NF‑κB, stem cell factor and vascular endothelial growth factor via western blot analysis. Computational network biology models were also applied to reveal the connections between the ten proteins examined. Combination treatment of IM with DCA caused extensive cell death (>75%) in K‑562 and considerable (>45%) in HCT‑116 (+/+p53) cultures, but less in K‑562R and HCT‑116 (‑/‑p53), with the latter deficient in full length p53 protein. Such treatment, markedly reduced reactive oxygen species levels, as measured by flow‑cytometry, in K‑562 cells and affected the oxidative phosphorylation and glycolytic biomarkers in all lines examined. These findings indicated, that targeting of cancer mitochondrial bioenergetics with such a combination treatment was very effective, although chemoresistance to IM in leukemia and the absence of a full length p53 in colorectal cells affected its impact.
Keywords: HCT‑116; K‑562; Warburg effect; bioenergetics; cancer; dichloroacetate; imatinib; mitochondria.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Persistent STAT5-mediated ROS production and involvement of aberrant p53 apoptotic signaling in the resistance of chronic myeloid leukemia to imatinib.Int J Mol Med. 2018 Jan;41(1):455-463. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2017.3205. Epub 2017 Oct 20. Int J Mol Med. 2018. PMID: 29115375
-
Imatinib inhibits the expression of SCO2 and FRATAXIN genes that encode mitochondrial proteins in human Bcr-Abl⁺ leukemia cells.Blood Cells Mol Dis. 2014 Jun-Aug;53(1-2):84-90. doi: 10.1016/j.bcmd.2014.03.001. Epub 2014 Apr 13. Blood Cells Mol Dis. 2014. PMID: 24726617
-
Homoharringtonine suppresses imatinib resistance via the Bcl-6/p53 pathway in chronic myeloid leukemia cell lines.Oncotarget. 2017 Jun 6;8(23):37594-37604. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.16731. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28410239 Free PMC article.
-
[Growth inhibition and differentiation of imatinib-resistant chronic myeloid leukemia cell induced by cell differentiation agent in vitro].Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2007 Dec 25;87(48):3399-405. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2007. PMID: 18476538 Chinese.
-
[MET/ERK and MET/JNK Pathway Activation Is Involved in BCR-ABL Inhibitor-resistance in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia].Yakugaku Zasshi. 2018;138(12):1461-1466. doi: 10.1248/yakushi.18-00142. Yakugaku Zasshi. 2018. PMID: 30504658 Review. Japanese.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
