Sulbactam-durlobactam: a β-lactam/β-lactamase inhibitor combination targeting Acinetobacter baumannii
- PMID: 38426849
- PMCID: PMC11229585
- DOI: 10.2217/fmb-2023-0248
Sulbactam-durlobactam: a β-lactam/β-lactamase inhibitor combination targeting Acinetobacter baumannii
Abstract
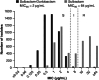
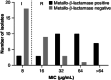
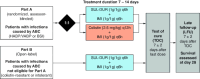
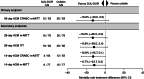
Sulbactam-durlobactam is a pathogen-targeted β-lactam/β-lactamase inhibitor combination that has been approved by the US FDA for the treatment of hospital-acquired and ventilator-associated bacterial pneumonia caused by susceptible isolates of Acinetobacter baumannii-calcoaceticus complex (ABC) in patients 18 years of age and older. Sulbactam is a penicillin derivative with antibacterial activity against Acinetobacter but is prone to hydrolysis by β-lactamases encoded by contemporary isolates. Durlobactam is a diazabicyclooctane β-lactamase inhibitor with activity against Ambler classes A, C and D serine β-lactamases that restores sulbactam activity both in vitro and in vivo against multidrug-resistant ABC. Sulbactam-durlobactam is a promising alternative therapy for the treatment of serious Acinetobacter infections, which can have high rates of mortality.
Keywords: Acinetobacter baumannii; carbapenem resistance; pneumonia; sulbactam–durlobactam; β-lactamase inhibitor.
Plain language summary
Sulbactam–durlobactam: a drug for treating lung infectionsAcinetobacter is a type of bacteria. One type, called CRAB, causes serious infections and can be fatal. CRAB is very hard to treat because most drugs no longer work. Sulbactam–durlobactam (SUL-DUR) is a drug that can kill CRAB. The US FDA approved SUL-DUR in May of 2023 for treating lung infections (pneumonia) caused by CRAB. This article explains how SUL-DUR works. Use of SUL-DUR and other drugs to treat these types of infections are discussed. In conclusion, SUL-DUR is a promising therapy for serious infections caused by CRAB.
Conflict of interest statement
SMM and JPO are employees of Innoviva Specialty Therapeutics, Inc., an affiliate of Entasis Therapeutics Inc., and own stock. JPM has no conflicts of interest to declare. NN reports grants/contracts from Merck and Shionogi, and consulting/speaker fees from Astellas, Beckman-Coulter, Paratek, and T2 Biosystems. KSK is a consultant for Entasis Therapeutics Inc., Shionogi, Merck, Abbvie, VenatoRx, MicuRx and GSK. The authors have no other competing interests or relevant affiliations with any organization or entity with the subject matter or materials discussed in the manuscript apart from those disclosed.
Figures
Similar articles
-
In Vitro Activity of Sulbactam-Durlobactam against Acinetobacter baumannii-calcoaceticus Complex Isolates Collected Globally in 2016 and 2017.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2020 Mar 24;64(4):e02534-19. doi: 10.1128/AAC.02534-19. Print 2020 Mar 24. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2020. PMID: 31988095 Free PMC article.
-
Unraveling sulbactam-durlobactam: insights into its role in combating infections caused by Acinetobacter baumannii.Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2025 Jan;23(1):67-78. doi: 10.1080/14787210.2024.2440018. Epub 2024 Dec 19. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2025. PMID: 39644103 Review.
-
In Vitro Activity of Sulbactam-Durlobactam against Global Isolates of Acinetobacter baumannii-calcoaceticus Complex Collected from 2016 to 2021.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2022 Sep 20;66(9):e0078122. doi: 10.1128/aac.00781-22. Epub 2022 Aug 25. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2022. PMID: 36005804 Free PMC article.
-
Sulbactam-durlobactam: A novel β-lactam-β-lactamase inhibitor combination targeting carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii infections.Pharmacotherapy. 2023 Jun;43(6):502-513. doi: 10.1002/phar.2802. Epub 2023 May 23. Pharmacotherapy. 2023. PMID: 37052117 Review.
-
Molecular drivers of resistance to sulbactam-durlobactam in contemporary clinical isolates of Acinetobacter baumannii.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2023 Nov 15;67(11):e0066523. doi: 10.1128/aac.00665-23. Epub 2023 Oct 16. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2023. PMID: 37843305 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
A Comprehensive Overview of Antibacterial Agents for Combating Multidrug-Resistant Bacteria: The Current Landscape, Development, Future Opportunities, and Challenges.Antibiotics (Basel). 2025 Feb 21;14(3):221. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics14030221. Antibiotics (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40149033 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Durlobactam to boost the clinical utility of standard of care β-lactams against Mycobacterium abscessus lung disease.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2025 Jan 31;69(1):e0104624. doi: 10.1128/aac.01046-24. Epub 2024 Nov 20. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2025. PMID: 39565116 Free PMC article.
-
Unseen Enemy: Mechanisms of Multidrug Antimicrobial Resistance in Gram-Negative ESKAPE Pathogens.Antibiotics (Basel). 2025 Jan 9;14(1):63. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics14010063. Antibiotics (Basel). 2025. PMID: 39858349 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Optimizing Treatment for Carbapenem-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii Complex Infections: A Review of Current Evidence.Infect Chemother. 2024 Jun;56(2):171-187. doi: 10.3947/ic.2024.0055. Infect Chemother. 2024. PMID: 38960737 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Mortality of Colistin Monotherapy vs. Colistin-Sulbactam for Carbapenem-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii Pneumonia: A Propensity Score Analysis.Infect Chemother. 2025 Mar;57(1):138-147. doi: 10.3947/ic.2024.0125. Infect Chemother. 2025. PMID: 40183660 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Centers for Disease Prevention and Control . Antibiotic Resistance Threats in the United States (2019). https://www.cdc.gov/drugresistance/biggest-threats.html (Accessed 14 January 2024).
-
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control . Rapid Risk Assessment: Carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii in Healthcare Settings (2016). https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/en/publications-data/rapid-risk-assessment-ca... (Accessed 14 January 2024).
-
- Lemos EV, de la Hoz FP, Einarson TRet al. . Carbapenem resistance and mortality in patients with Acinetobacter baumannii infection: systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 20(5), 416–423 (2014). - PubMed
-
- Falcone M, Tiseo G, Carbonara Set al. . Mortality Attributable to Bloodstream Infections Caused by Different Carbapenem-Resistant Gram-Negative Bacilli: Results From a Nationwide Study in Italy (ALARICO Network). Clin. Infect. Dis. 76(12), 2059–2069 (2023). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
