Recurrent infections drive persistent bladder dysfunction and pain via sensory nerve sprouting and mast cell activity
- PMID: 38427717
- PMCID: PMC11149582
- DOI: 10.1126/sciimmunol.adi5578
Recurrent infections drive persistent bladder dysfunction and pain via sensory nerve sprouting and mast cell activity
Abstract
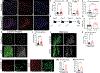
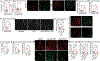
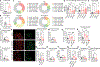
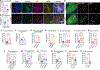
Urinary tract infections (UTIs) account for almost 25% of infections in women. Many are recurrent (rUTI), with patients frequently experiencing chronic pelvic pain and urinary frequency despite clearance of bacteriuria after antibiotics. To elucidate the basis for these bacteria-independent bladder symptoms, we examined the bladders of patients with rUTI. We noticed a notable increase in neuropeptide content in the lamina propria and indications of enhanced nociceptive activity. In mice subjected to rUTI, we observed sensory nerve sprouting that was associated with nerve growth factor (NGF) produced by recruited monocytes and tissue-resident mast cells. Treatment of rUTI mice with an NGF-neutralizing antibody prevented sprouting and alleviated pelvic sensitivity, whereas instillation of native NGF into naïve mice bladders mimicked nerve sprouting and pain behavior. Nerve activation, pain, and urinary frequency were each linked to the presence of proximal mast cells, because mast cell deficiency or treatment with antagonists against receptors of several direct or indirect mast cell products was each effective therapeutically. Thus, our findings suggest that NGF-driven sensory sprouting in the bladder coupled with chronic mast cell activation represents an underlying mechanism driving bacteria-independent pain and voiding defects experienced by patients with rUTI.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests
The authors declare they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Foxman B, Epidemiology of urinary tract infections: incidence, morbidity, and economic costs. Am J Med 113 Suppl 1A, 5S–13S (2002). - PubMed
-
- Foxman B, Barlow R, D’Arcy H, Gillespie B, Sobel JD, Urinary tract infection: self-reported incidence and associated costs. Ann Epidemiol 10, 509–515 (2000). - PubMed
-
- Tandogdu Z, Wagenlehner FM, Global epidemiology of urinary tract infections. Curr Opin Infect Dis 29, 73–79 (2016). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

