A predictive coding model of the N400
- PMID: 38428168
- PMCID: PMC10984641
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cognition.2024.105755
A predictive coding model of the N400
Abstract
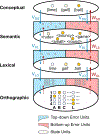
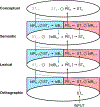
The N400 event-related component has been widely used to investigate the neural mechanisms underlying real-time language comprehension. However, despite decades of research, there is still no unifying theory that can explain both its temporal dynamics and functional properties. In this work, we show that predictive coding - a biologically plausible algorithm for approximating Bayesian inference - offers a promising framework for characterizing the N400. Using an implemented predictive coding computational model, we demonstrate how the N400 can be formalized as the lexico-semantic prediction error produced as the brain infers meaning from the linguistic form of incoming words. We show that the magnitude of lexico-semantic prediction error mirrors the functional sensitivity of the N400 to various lexical variables, priming, contextual effects, as well as their higher-order interactions. We further show that the dynamics of the predictive coding algorithm provides a natural explanation for the temporal dynamics of the N400, and a biologically plausible link to neural activity. Together, these findings directly situate the N400 within the broader context of predictive coding research. More generally, they raise the possibility that the brain may use the same computational mechanism for inference across linguistic and non-linguistic domains.
Keywords: Bayesian inference; Language comprehension; Orthographic; Prediction; Prediction error; Semantic.
Copyright © 2024 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


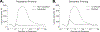
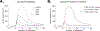

Similar articles
-
An implemented predictive coding model of lexico-semantic processing explains the dynamics of univariate and multivariate activity within the left ventromedial temporal lobe during reading comprehension.Neuroimage. 2025 Mar;308:120977. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2024.120977. Epub 2024 Dec 16. Neuroimage. 2025. PMID: 39694345 Free PMC article.
-
Neural evidence for Bayesian trial-by-trial adaptation on the N400 during semantic priming.Cognition. 2019 Jun;187:10-20. doi: 10.1016/j.cognition.2019.01.001. Epub 2019 Feb 20. Cognition. 2019. PMID: 30797099 Free PMC article.
-
Priming production: Neural evidence for enhanced automatic semantic activity preceding language production in schizophrenia.Neuroimage Clin. 2017 Dec 21;18:74-85. doi: 10.1016/j.nicl.2017.12.026. eCollection 2018. Neuroimage Clin. 2017. PMID: 29387525 Free PMC article.
-
Getting real about semantic illusions: rethinking the functional role of the P600 in language comprehension.Brain Res. 2012 Mar 29;1446:127-43. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2012.01.055. Epub 2012 Feb 2. Brain Res. 2012. PMID: 22361114 Review.
-
Neural mechanisms of language comprehension: challenges to syntax.Brain Res. 2007 May 18;1146:23-49. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2006.12.063. Epub 2006 Dec 23. Brain Res. 2007. PMID: 17400197 Review.
Cited by
-
Convergent neural signatures of speech prediction error are a biological marker for spoken word recognition.Nat Commun. 2024 Nov 18;15(1):9984. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-53782-5. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 39557848 Free PMC article.
-
Unpleasant words can affect the detection of morphosyntactic errors: An ERP study on individual differences.Psychophysiology. 2024 Dec;61(12):e14663. doi: 10.1111/psyp.14663. Epub 2024 Jul 31. Psychophysiology. 2024. PMID: 39086024 Free PMC article.
-
An implemented predictive coding model of lexico-semantic processing explains the dynamics of univariate and multivariate activity within the left ventromedial temporal lobe during reading comprehension.Neuroimage. 2025 Mar;308:120977. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2024.120977. Epub 2024 Dec 16. Neuroimage. 2025. PMID: 39694345 Free PMC article.
-
Misspelled-Word Reading Modulates Late Cortical Dynamics.Hum Brain Mapp. 2025 Jun 1;46(8):e70247. doi: 10.1002/hbm.70247. Hum Brain Mapp. 2025. PMID: 40503587 Free PMC article.
-
Contextual expectations in the real-world modulate low-frequency neural oscillations.Imaging Neurosci (Camb). 2025 May 7;3:imag_a_00568. doi: 10.1162/imag_a_00568. eCollection 2025 May 7. Imaging Neurosci (Camb). 2025. PMID: 40433299 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baggio G, & Hagoort P (2011). The balance between memory and unification in semantics: A dynamic account of the N400. Language and Cognitive Processes, 26(9), 1338–1367. doi: 10.1080/01690965.2010.542671 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

