Myogenic exosome miR-140-5p modulates skeletal muscle regeneration and injury repair by regulating muscle satellite cells
- PMID: 38428405
- PMCID: PMC10968704
- DOI: 10.18632/aging.205617
Myogenic exosome miR-140-5p modulates skeletal muscle regeneration and injury repair by regulating muscle satellite cells
Abstract
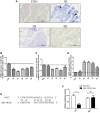
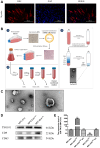
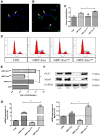
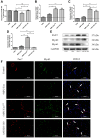
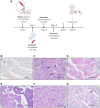
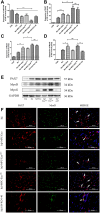
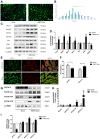
Muscle satellite cells (SCs) play a crucial role in the regeneration and repair of skeletal muscle injuries. Previous studies have shown that myogenic exosomes can enhance satellite cell proliferation, while the expression of miR-140-5p is significantly reduced during the repair process of mouse skeletal muscle injuries induced by BaCl2. This study aims to investigate the potential of myogenic exosomes carrying miR-140-5p inhibitors to activate SCs and influence the regeneration of injured muscles. Myogenic progenitor cell exosomes (MPC-Exo) and contained miR-140-5p mimics/inhibitors myogenic exosomes (MPC-Exo140+ and MPC-Exo140-) were employed to treat SCs and use the model. The results demonstrate that miR-140-5p regulates SC proliferation by targeting Pax7. Upon the addition of MPC-Exo and MPC-Exo140-, Pax7 expression in SCs significantly increased, leading to the transition of the cell cycle from G1 to S phase and an enhancement in cell proliferation. Furthermore, the therapeutic effect of MPC-Exo140- was validated in animal model, where the expression of muscle growth-related genes substantially increased in the gastrocnemius muscle. Our research demonstrates that MPC-Exo140- can effectively activate dormant muscle satellite cells, initiating their proliferation and differentiation processes, ultimately leading to the formation of new skeletal muscle cells and promoting skeletal muscle repair and remodeling.
Keywords: exosomes; miR-140-5p; muscle injury repair; muscle satellite cells; regeneration.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Exosomes Secreted During Myogenic Differentiation of Human Fetal Cartilage-Derived Progenitor Cells Promote Skeletal Muscle Regeneration through miR-145-5p.Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2024 Apr;21(3):487-497. doi: 10.1007/s13770-023-00618-w. Epub 2024 Jan 31. Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2024. PMID: 38294592 Free PMC article.
-
Hypoxic preconditioning-engineered bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes promote muscle satellite cell activation and skeletal muscle regeneration via the miR-210-3p/KLF7 mechanism.Int Immunopharmacol. 2024 Dec 5;142(Pt B):113143. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2024.113143. Epub 2024 Sep 21. Int Immunopharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39306891
-
microRNA-1 and microRNA-206 regulate skeletal muscle satellite cell proliferation and differentiation by repressing Pax7.J Cell Biol. 2010 Sep 6;190(5):867-79. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200911036. J Cell Biol. 2010. PMID: 20819939 Free PMC article.
-
The role of satellite and other functional cell types in muscle repair and regeneration.J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 2019 Mar;40(1):1-8. doi: 10.1007/s10974-019-09511-3. Epub 2019 Apr 9. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 2019. PMID: 30968305 Review.
-
The roles of miRNAs in adult skeletal muscle satellite cells.Free Radic Biol Med. 2023 Nov 20;209(Pt 2):228-238. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2023.10.403. Epub 2023 Oct 24. Free Radic Biol Med. 2023. PMID: 37879420 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Recent Advances of Exosomes Derived from Skeletal Muscle and Crosstalk with Other Tissues.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Oct 10;25(20):10877. doi: 10.3390/ijms252010877. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39456658 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Whitham M, Parker BL, Friedrichsen M, Hingst JR, Hjorth M, Hughes WE, Egan CL, Cron L, Watt KI, Kuchel RP, Jayasooriah N, Estevez E, Petzold T, et al.. Extracellular Vesicles Provide a Means for Tissue Crosstalk during Exercise. Cell Metab. 2018; 27:237–51.e4. 10.1016/j.cmet.2017.12.001 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

