Causal effects of gut microbiota on autism spectrum disorder: A two-sample mendelian randomization study
- PMID: 38428908
- PMCID: PMC10906619
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000037284
Causal effects of gut microbiota on autism spectrum disorder: A two-sample mendelian randomization study
Abstract
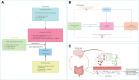
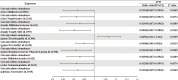
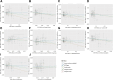
There is increasing evidence that alterations in gut microbiota (GM) composition are associated with autism spectrum disorder (ASD), but no reliable causal relationship has been established. Therefore, a 2-sample Mendelian randomization (MR) study was conducted to reveal a potential causal relationship between GM and ASD. Instrumental variables for 211 GM taxa were obtained from genome-wide association studies (GWAS) and Mendelian randomization studies to estimate their impact on ASD risk in the iPSYCH-PGC GWAS dataset (18,382 ASD cases and 27,969 controls). Inverse variance weighted (IVW) is the primary method for causality analysis, and several sensitivity analyses validate MR results. Among 211 GM taxa, IVW results confirmed that Tenericutes (P value = .0369), Mollicutes (P value = .0369), Negativicutes (P value = .0374), Bifidobacteriales (P value = .0389), Selenomonadales (P value = .0374), Bifidobacteriaceae (P value = .0389), Family XIII (P value = .0149), Prevotella7 (P value = .0215), Ruminococcaceae NK4A214 group (P value = .0205) were potential protective factors for ASD. Eisenbergiella (P value = .0159) was a possible risk factor for ASD. No evidence of heterogeneous, pleiotropic, or outlier single-nucleotide polymorphism was detected. Additionally, further sensitivity analysis verified the robustness of the above results. We confirm a potential causal relationship between certain gut microbes and ASD, providing new insights into how gut microbes mediate ASD. The association between them needs to be further explored and will provide new ideas for the prevention and treatment of ASD.
Copyright © 2024 the Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures