Comparison of individual and ensemble machine learning models for prediction of sulphate levels in untreated and treated Acid Mine Drainage
- PMID: 38429461
- PMCID: PMC10907470
- DOI: 10.1007/s10661-024-12467-8
Comparison of individual and ensemble machine learning models for prediction of sulphate levels in untreated and treated Acid Mine Drainage
Abstract
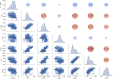
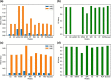
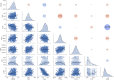
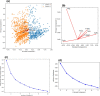
Machine learning was used to provide data for further evaluation of potential extraction of octathiocane (S8), a commercially useful by-product, from Acid Mine Drainage (AMD) by predicting sulphate levels in an AMD water quality dataset. Individual ML regressor models, namely: Linear Regression (LR), Least Absolute Shrinkage and Selection Operator (LASSO), Ridge (RD), Elastic Net (EN), K-Nearest Neighbours (KNN), Support Vector Regression (SVR), Decision Tree (DT), Extreme Gradient Boosting (XGBoost), Random Forest (RF), Multi-Layer Perceptron Artificial Neural Network (MLP) and Stacking Ensemble (SE-ML) combinations of these models were successfully used to predict sulphate levels. A SE-ML regressor trained on untreated AMD which stacked seven of the best-performing individual models and fed them to a LR meta-learner model was found to be the best-performing model with a Mean Squared Error (MSE) of 0.000011, Mean Absolute Error (MAE) of 0.002617 and R2 of 0.9997. Temperature (°C), Total Dissolved Solids (mg/L) and, importantly, iron (mg/L) were highly correlated to sulphate (mg/L) with iron showing a strong positive linear correlation that indicated dissolved products from pyrite oxidation. Ensemble learning (bagging, boosting and stacking) outperformed individual methods due to their combined predictive accuracies. Surprisingly, when comparing SE-ML that combined all models with SE-ML that combined only the best-performing models, there was only a slight difference in model accuracies which indicated that including bad-performing models in the stack had no adverse effect on its predictive performance.
Keywords: Acid Mine Drainage; Environmental chemistry; Machine learning; Regression; Stacking ensemble machine learning; Sulphate.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures







References
-
- Alzubi J, Nayyar A, Kumar A. Machine learning from theory to algorithms: An overview. Journal of Physics: Conference Series. 2018;1142:012012. doi: 10.1088/1742-6596/1142/1/012012. - DOI
-
- Arora, S., & Keshari, A. K. (2023). Implementing machine learning algorithm to model reaeration coefficient of urbanized rivers. Environmental Modeling & Assessment10.1007/s10666-023-09895-0
-
- Awad, M., & Khanna, R. (2015). Support vector regression. In Efficient Learning Machines (67–80). Berkeley, CA: Apress. 10.1007/978-1-4302-5990-9_4
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

