Evaluating the comprehensive diagnosis efficiency of lung cancer, including measurement of SHOX2 and RASSF1A gene methylation
- PMID: 38429660
- PMCID: PMC10908052
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-024-12022-1
Evaluating the comprehensive diagnosis efficiency of lung cancer, including measurement of SHOX2 and RASSF1A gene methylation
Abstract
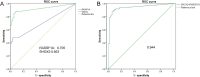
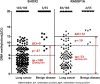
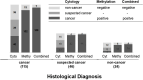
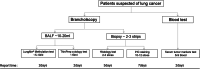
Methylation of the promoters of SHOX2 and RASSF1A (LungMe®) exhibits promise as a potential molecular biomarker for diagnosing lung cancer. This study sought to assess the aberrant methylation of SHOX2 and RASSF1A in broncho-exfoliated cells (BEC) and compare it with conventional cytology, histology examination, immunohistochemistry, and serum tumor markers to evaluate the overall diagnostic efficiency for lung cancer. This study recruited 240 patients, including 185 malignant cases and 55 benign cases. In our observation, we noted a slight reduction in the detection sensitivity, however, the ΔCt method exhibited a significant enhancement in specificity when compared to Ct judgment. Consequently, the ΔCt method proves to be a more appropriate approach for interpreting methylation results. The diagnostic sensitivity of cytology and histology was in ranged from 20.0%-35.1% and 42.9%-80%, respectively, while the positive detection rate of LungMe® methylation ranged from 70.0% to 100%. Additionally, our findings indicate a higher prevalence of SHOX2( +) among patients exhibiting medium and high expression of Ki67 (P < 0.01), as opposed to those with low expression of Ki67, but RASSF1A methylation did not show this phenomenon (P = 0.35). Furthermore, CEA, SCCA, and CYFRA21-1 showed positive detection rates of 48.8%, 26.2%, and 55.8%, respectively. Finally, we present a comprehensive lung cancer diagnostic work-up, including LumgMe® methylation. The combined analysis of SHOX2 and RASSF1A methylation serves as a powerful complement and extension to conventional methods, enhancing the accuracy of a lung cancer diagnosis with satisfactory sensitivity and specificity.
Keywords: DNA methylation; Diagnosis; Lung cancer; RASSF1A; SHOX2.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
BS was employed by Tellgen Corporation, Shanghai, China. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted without any commercial or financial relationships that could be perceived as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Association of DNA methylation of RASSF1A and SHOX2 with lung cancer risk: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2024 Dec 13;103(50):e40042. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000040042. Medicine (Baltimore). 2024. PMID: 39686414 Free PMC article.
-
SHOX2 and RASSF1A methylation in diagnosing malignant pleural effusion induced by lung cancer.Clin Chim Acta. 2025 May 15;572:120273. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2025.120273. Epub 2025 Mar 29. Clin Chim Acta. 2025. PMID: 40164346
-
Association of the SHOX2 and RASSF1A methylation levels with the pathological evolution of early-stage lung adenocarcinoma.BMC Cancer. 2024 Jun 5;24(1):687. doi: 10.1186/s12885-024-12452-x. BMC Cancer. 2024. PMID: 38840077 Free PMC article.
-
Enhancing the precision of auxiliary diagnosis for lung cancer through use of SHOX2 and RASSF1A methylation status in lung biopsy and lymph node biopsy specimens.Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2025 Mar 31;14(3):897-911. doi: 10.21037/tlcr-2024-1082. Epub 2025 Mar 24. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2025. PMID: 40248719 Free PMC article.
-
Meta-analysis of the accuracy for RASSF1A methylation in bronchial aspirates for the diagnosis of lung cancer.PLoS One. 2024 Jul 25;19(7):e0299447. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0299447. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39052646 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Catching cancer signals in the blood: Innovative pathways for early esophageal cancer diagnosis.World J Gastroenterol. 2025 Mar 14;31(10):101838. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i10.101838. World J Gastroenterol. 2025. PMID: 40093671 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic performance of SHOX2 and RASSF1A gene methylation assays in malignant pleural effusion: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Cancer Cytopathol. 2025 Aug;133(8):e70031. doi: 10.1002/cncy.70031. Cancer Cytopathol. 2025. PMID: 40614167 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Association of DNA methylation of RASSF1A and SHOX2 with lung cancer risk: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2024 Dec 13;103(50):e40042. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000040042. Medicine (Baltimore). 2024. PMID: 39686414 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic modifications in early stage lung cancer: pathogenesis, biomarkers, and early diagnosis.MedComm (2020). 2025 Feb 21;6(3):e70080. doi: 10.1002/mco2.70080. eCollection 2025 Mar. MedComm (2020). 2025. PMID: 39991629 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epigenomic Echoes-Decoding Genomic and Epigenetic Instability to Distinguish Lung Cancer Types and Predict Relapse.Epigenomes. 2025 Feb 5;9(1):5. doi: 10.3390/epigenomes9010005. Epigenomes. 2025. PMID: 39982247 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

