Differential modulation of PI3K/Akt/mTOR activity by EGFR inhibitors: A rationale for co-targeting EGFR and PI3K in cisplatin-resistant HNSCC
- PMID: 38429897
- PMCID: PMC11003831
- DOI: 10.1002/hed.27718
Differential modulation of PI3K/Akt/mTOR activity by EGFR inhibitors: A rationale for co-targeting EGFR and PI3K in cisplatin-resistant HNSCC
Abstract
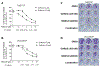
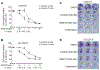
Purpose: To find a new strategy to treat cisplatin-resistant head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC), we investigated the effects of EGFR inhibitors on the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway and determined the efficacy of EGFR inhibitors in combination with PI3K inhibitors to suppress cell proliferation in cisplatin-resistant-HNSCC.
Methods: The cisplatin-resistant HNSCC cell lines were treated with four FDA approved EGFR inhibitors, which included Gefitinb or Erlotinib alone, or in combination with the pan-PI3K inhibitor, BKM120. Phosphorylation and total protein levels of cells were assessed by Western blot analysis. Cell proliferation was examined by MTS assay. Apoptosis was analyzed by flow cytometry.
Results: Cisplatin-resistant HNSCC cells were also resistant to EGFR inhibitors. However, a combination of EGFR inhibitors with PI3K inhibitor BKM120 dramatically improved the efficacy of EGFR inhibitors to inhibit cell proliferation and induce apoptosis. Furthermore, treatment with EGFR inhibitors differentially affected the phosphorylation of Akt and mTOR, which included partial inhibition, no inhibition, and induction. A combination of EGFR inhibitors and BKM120 completely blocked phosphorylation of EGFR, Akt, and S6K (an mTOR target).
Conclusion: Our data provided a rationale for EGFR inhibitors in combination with PI3K inhibitors to treat cisplatin-resistant HNSCC.
Keywords: EGFR; EGFR inhibitor; HNSCC; PI3K; PI3K inhibitors; cisplatin resistance; targeted therapy.
© 2024 Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure of Potential Conflicts of Interest
No potential conflicts of interest were disclosed.
Figures
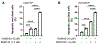
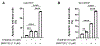

Similar articles
-
Exploring the antiproliferative effect of PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway and CDK4/6 inhibitors in human papillomavirus‑positive and ‑negative head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cell lines.Int J Oncol. 2025 Feb;66(2):13. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2025.5719. Epub 2025 Jan 10. Int J Oncol. 2025. PMID: 39791215 Free PMC article.
-
Simultaneously targeting ErbB family kinases and PI3K in HPV-positive head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.Oral Oncol. 2022 Aug;131:105939. doi: 10.1016/j.oraloncology.2022.105939. Epub 2022 Jun 3. Oral Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35667295
-
A positive feedback loop involving EGFR/Akt/mTORC1 and IKK/NF-kB regulates head and neck squamous cell carcinoma proliferation.Oncotarget. 2016 May 31;7(22):31892-906. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.7441. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 26895469 Free PMC article.
-
The PI3K/Akt/mTORC signaling axis in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: Possibilities for therapeutic interventions either as single agents or in combination with conventional therapies.IUBMB Life. 2021 Apr;73(4):618-642. doi: 10.1002/iub.2446. Epub 2021 Feb 4. IUBMB Life. 2021. PMID: 33476088 Review.
-
Targeting EGFR-PI3K-AKT-mTOR signaling enhances radiosensitivity in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2015 Jun;19(6):795-805. doi: 10.1517/14728222.2015.1012157. Epub 2015 Feb 5. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2015. PMID: 25652792 Review.
Cited by
-
Targeted inhibition of the PTEN/PI3K/AKT pathway by YSV induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in oral squamous cell carcinoma.J Transl Med. 2025 Feb 3;23(1):145. doi: 10.1186/s12967-025-06169-z. J Transl Med. 2025. PMID: 39901205 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular insights into immune evasion in head and neck squamous cell carcinomas: Toward a promising treatment strategy.Oncol Res. 2025 May 29;33(6):1271-1282. doi: 10.32604/or.2025.062207. eCollection 2025. Oncol Res. 2025. PMID: 40486875 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Research progress on ferroptosis in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.J Mol Histol. 2025 Mar 17;56(2):109. doi: 10.1007/s10735-025-10381-y. J Mol Histol. 2025. PMID: 40095205 Review.
References
-
- Nwizu T, Adelstein D. Pharmacotherapy of head and neck cancer. Expert opinion on pharmacotherapy 2015;16:2409–2422. - PubMed
-
- Colevas AD. Systemic Therapy for Metastatic or Recurrent Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Head and Neck. Journal of the National Comprehensive Cancer Network : JNCCN 2015;13:e37–48. - PubMed
-
- Milas L, Mason KA, Liao Z, Ang KK. Chemoradiotherapy: emerging treatment improvement strategies. Head & neck 2003;25:152–167. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

