Real-time breast lesion classification combining diffuse optical tomography frequency domain data and BI-RADS assessment
- PMID: 38430216
- PMCID: PMC11065578
- DOI: 10.1002/jbio.202300483
Real-time breast lesion classification combining diffuse optical tomography frequency domain data and BI-RADS assessment
Abstract
Ultrasound (US)-guided diffuse optical tomography (DOT) has demonstrated potential for breast cancer diagnosis, in which real-time or near real-time diagnosis with high accuracy is desired. However, DOT's relatively slow data processing and image reconstruction speeds have hindered real-time diagnosis. Here, we propose a real-time classification scheme that combines US breast imaging reporting and data system (BI-RADS) readings and DOT frequency domain measurements. A convolutional neural network is trained to generate malignancy probability scores from DOT measurements. Subsequently, these scores are integrated with BI-RADS assessments using a support vector machine classifier, which then provides the final diagnostic output. An area under the receiver operating characteristic curve of 0.978 is achieved in distinguishing between benign and malignant breast lesions in patient data without image reconstruction.
Keywords: breast cancer diagnosis; diffuse optical tomography; frequency domain optical systems.
© 2024 Wiley‐VCH GmbH.
Figures

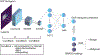


References
-
- In Cancer Facts & Figures 2022, American Cancer Society.
-
- Bakker MF, de Lange SV, Pijnappel RM, Mann RM, Peeters PHM, Monninkhof EM, Emaus MJ, Loo CE, Bisschops RHC, Lobbes MBI, de Jong MDF, Duvivier KM, Veltman J, Karssemeijer N, de Koning HJ, van Diest PJ, Mali WPTM, van den Bosch MAAJ, Veldhuis WB and van Gils CH, N. Engl. J. Med, 2019, 381, 2091–2102. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

