Assessing immunogenicity of CRISPR-NCas9 engineered strain against porcine epidemic diarrhea virus
- PMID: 38430229
- PMCID: PMC10908614
- DOI: 10.1007/s00253-023-12989-0
Assessing immunogenicity of CRISPR-NCas9 engineered strain against porcine epidemic diarrhea virus
Erratum in
-
Correction: Assessing immunogenicity of CRISPR‑NCas9 engineered strain against porcine epidemic diarrhea virus.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2024 May 24;108(1):341. doi: 10.1007/s00253-024-13192-5. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 38789550 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
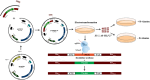
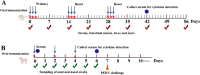
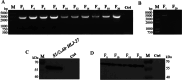
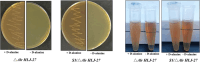
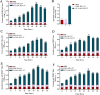
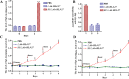
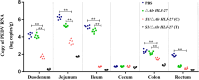
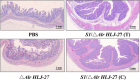
Porcine epidemic diarrhea (PED) caused by porcine epidemic diarrhea virus (PEDV), is an acute and highly infectious disease, resulting in substantial economic losses in the pig industry. Given that PEDV primarily infects the mucosal surfaces of the intestinal tract, it is crucial to improve the mucosal immunity to prevent viral invasion. Lactic acid bacteria (LAB) oral vaccines offer unique advantages and potential applications in combatting mucosal infectious diseases, making them an ideal approach for controlling PED outbreaks. However, traditional LAB oral vaccines use plasmids for exogenous protein expression and antibiotic genes as selection markers. Antibiotic genes can be diffused through transposition, transfer, or homologous recombination, resulting in the generation of drug-resistant strains. To overcome these issues, genome-editing technology has been developed to achieve gene expression in LAB genomes. In this study, we used the CRISPR-NCas9 system to integrate the PEDV S1 gene into the genome of alanine racemase-deficient Lactobacillus paracasei △Alr HLJ-27 (L. paracasei △Alr HLJ-27) at the thymidylate synthase (thyA) site, generating a strain, S1/△Alr HLJ-27. We conducted immunization assays in mice and piglets to evaluate the level of immune response and evaluated its protective effect against PEDV through challenge tests in piglets. Oral administration of the strain S1/△Alr HLJ-27 in mice and piglets elicited mucosal, humoral, and cellular immune responses. The strain also exhibited a certain level of resistance against PEDV infection in piglets. These results demonstrate the potential of S1/△Alr HLJ-27 as an oral vaccine candidate for PEDV control. KEY POINTS: • A strain S1/△Alr HLJ-27 was constructed as the candidate for an oral vaccine. • Immunogenicity response and challenge test was carried out to analyze the ability of the strain. • The strain S1/△Alr HLJ-27 could provide protection for piglets to a certain extent.
Keywords: CRISPR-Cas9; Genome expression; Lactic acid bacteria; Oral vaccine; PEDV S1 gene.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Evaluation of the immunogenicity of auxotrophic Lactobacillus with CRISPR-Cas9D10A system-mediated chromosomal editing to express porcine rotavirus capsid protein VP4.Virulence. 2022 Dec;13(1):1315-1330. doi: 10.1080/21505594.2022.2107646. Virulence. 2022. PMID: 35920261 Free PMC article.
-
Recombinant Lactobacillus acidophilus expressing S1 and S2 domains of porcine epidemic diarrhea virus could improve the humoral and mucosal immune levels in mice and sows inoculated orally.Vet Microbiol. 2020 Sep;248:108827. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2020.108827. Epub 2020 Aug 16. Vet Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32891955 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of the Immunogenicity in Mice Orally Immunized with Recombinant Lactobacillus casei Expressing Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus S1 Protein.Viruses. 2022 Apr 25;14(5):890. doi: 10.3390/v14050890. Viruses. 2022. PMID: 35632632 Free PMC article.
-
A Comprehensive View on the Protein Functions of Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus.Genes (Basel). 2024 Jan 26;15(2):165. doi: 10.3390/genes15020165. Genes (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38397155 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Advances in reverse genetics to treat porcine epidemic diarrhea virus].Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao. 2017 Feb 25;33(2):205-216. doi: 10.13345/j.cjb.160282. Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao. 2017. PMID: 28956377 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
CRISPR/Cas9-mediated genomic insertion of functional genes into Lactiplantibacillus plantarum WCFS1.Microbiol Spectr. 2025 Feb 4;13(2):e0202524. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.02025-24. Epub 2025 Jan 16. Microbiol Spectr. 2025. PMID: 39817779 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in porcine epidemic diarrhea virus research: genome, epidemiology, vaccines, and detection methods.Discov Nano. 2025 Mar 3;20(1):48. doi: 10.1186/s11671-025-04220-y. Discov Nano. 2025. PMID: 40029472 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metabolic engineering of Lactobacilli spp. for disease treatment.Microb Cell Fact. 2025 Mar 6;24(1):53. doi: 10.1186/s12934-025-02682-4. Microb Cell Fact. 2025. PMID: 40050843 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Agarwal N, Gupta R (2021) History, evolution and classification of crispr-cas associated systems-sciencedirect. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci 179:11–76. 10.1016/bs.pmbts.2020.12.012 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

