Treatment Patterns with Mirabegron and Antimuscarinics for Overactive Bladder: A Prospective, Registry Study in Taiwan and South Korea (FAITH)
- PMID: 38430402
- PMCID: PMC10960886
- DOI: 10.1007/s12325-024-02784-2
Treatment Patterns with Mirabegron and Antimuscarinics for Overactive Bladder: A Prospective, Registry Study in Taiwan and South Korea (FAITH)
Abstract
Introduction: This study aimed to assess overactive bladder (OAB) treatment patterns and factors associated with effectiveness and persistence.
Methods: A prospective, longitudinal, observational registry study of adults starting OAB therapy with mirabegron or antimuscarinics was undertaken. Primary endpoints were time from treatment initiation to discontinuation/switching; proportion who discontinued/switched; and reasons for discontinuation/switching. Secondary endpoints included OAB Symptom Score (OABSS), OAB Questionnaire: Short Form, and OAB Bladder Assessment Tool scores; factors associated with effectiveness and persistence; and safety.
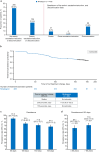
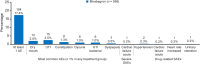
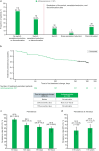
Results: In total, 556 patients initiating mirabegron and 250 initiating antimuscarinics were enrolled. There was no treatment switch, change, or discontinuation in 68.5% of the mirabegron initiator group and median time to treatment change was not reached. Mean initial treatment duration was 130.8 days. In multivariable models, baseline OABSS was the only variable significantly associated with change from baseline in OABSS, and patients with mild and moderate OAB had significantly better persistence with mirabegron than those with severe OAB. Urinary tract infection was the most common adverse event with mirabegron. There was no treatment switch, change, or discontinuation in 60.4% of the antimuscarinics initiator group and median time to treatment change was not reached. Solifenacin was the most frequent initial treatment (66.0%). Mean treatment duration was 122.2 days. In multivariable models, baseline OABSS was the only variable significantly associated with change from baseline in OABSS, while patients with OAB medication in the 12 months before enrollment had significantly better persistence with antimuscarinics than those with no previous OAB medication. Dry mouth was the most common adverse event with antimuscarinics.
Conclusions: Mirabegron and solifenacin were commonly prescribed as first-line OAB medications. There was no treatment switch, change, or discontinuation in more than 60% of the mirabegron initiator and antimuscarinics initiator groups. Mean initial treatment duration was 130.8 days and 122.2 days for mirabegron and antimuscarinics, respectively. Graphical Abstract available for this article.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT03572231.
Keywords: Non-interventional; Overactive bladder; Persistence; Prospective study; β3-adrenoceptor agonist.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Seung-June Oh has received grant support from Astellas and was a moderator of the “Astellas Asia-Oceania closed symposium” held on February 15, 2019, in Seoul, South Korea. Sung Tae Cho, Hann-Chorng Kuo, Eric Chieh-Lung Chou, Yu-Chao Hsu, and Kyu-Sung Lee have nothing to disclose outside of the submitted work. Farid Hadi is an employee of Astellas Pharma, Inc. Yi Song and Budiwan Sumarsono were employees at Astellas Pharma, Inc. at the time of the study.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Safety and efficacy of mirabegron as 'add-on' therapy in patients with overactive bladder treated with solifenacin: a post-marketing, open-label study in Japan (MILAI study).BJU Int. 2015 Oct;116(4):612-22. doi: 10.1111/bju.13068. Epub 2015 Apr 23. BJU Int. 2015. PMID: 25639296 Clinical Trial.
-
Persistence and Adherence with Mirabegron versus Antimuscarinic Agents in Patients with Overactive Bladder: A Retrospective Observational Study in UK Clinical Practice.Eur Urol. 2017 Sep;72(3):389-399. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2017.01.037. Epub 2017 Feb 11. Eur Urol. 2017. PMID: 28196724
-
Factors Associated with Improvements in Patient-Reported Outcomes During Mirabegron or Antimuscarinic Treatment of Overactive Bladder Syndrome: A Registry Study (PERSPECTIVE).Adv Ther. 2019 Aug;36(8):1906-1921. doi: 10.1007/s12325-019-00994-7. Epub 2019 Jun 20. Adv Ther. 2019. PMID: 31222714 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative efficacy and safety of medical treatments for the management of overactive bladder: a systematic literature review and mixed treatment comparison.Eur Urol. 2014 Apr;65(4):755-65. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2013.11.010. Epub 2013 Nov 18. Eur Urol. 2014. PMID: 24275310
-
Real-world persistence and adherence to oral antimuscarinics and mirabegron in patients with overactive bladder (OAB): a systematic literature review.BMJ Open. 2018 Nov 21;8(11):e021889. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2018-021889. BMJ Open. 2018. PMID: 30467131 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Coyne KS, Sexton CC, Irwin DE, Kopp ZS, Kelleher CJ, Milsom I. The impact of overactive bladder, incontinence and other lower urinary tract symptoms on quality of life, work productivity, sexuality and emotional well-being in men and women: results from the EPIC study. BJU Int. 2008;101(11):1388–1395. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-410X.2008.07601.x. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

