Elesclomol Loaded Copper Oxide Nanoplatform Triggers Cuproptosis to Enhance Antitumor Immunotherapy
- PMID: 38430531
- PMCID: PMC11095170
- DOI: 10.1002/advs.202309984
Elesclomol Loaded Copper Oxide Nanoplatform Triggers Cuproptosis to Enhance Antitumor Immunotherapy
Abstract
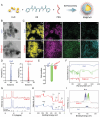
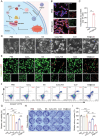
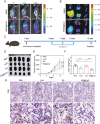
The induction of cuproptosis, a recently identified form of copper-dependent immunogenic cell death, is a promising approach for antitumor therapy. However, sufficient accumulation of intracellular copper ions (Cu2+) in tumor cells is essential for inducing cuproptosis. Herein, an intelligent cuproptosis-inducing nanosystem is constructed by encapsulating copper oxide (CuO) nanoparticles with the copper ionophore elesclomol (ES). After uptake by tumor cells, ES@CuO is degraded to release Cu2+ and ES to synergistically trigger cuproptosis, thereby significantly inhibiting the tumor growth of murine B16 melanoma cells. Moreover, ES@CuO further promoted cuproptosis-mediated immune responses and reprogrammed the immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment by increasing the number of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes and secreted inflammatory cytokines. Additionally, combining ES@CuO with programmed cell death-1 (PD-1) immunotherapy substantially increased the antitumor efficacy in murine melanoma. Overall, the findings of this study can lead to the use of a novel strategy for cuproptosis-mediated antitumor therapy, which may enhance the efficacy of immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy.
Keywords: CuO; PD‐1; cuproptosis; elesclomol; immunotherapy.
© 2024 The Authors. Advanced Science published by Wiley‐VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- 82272172/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 81972261/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 2021C03120/Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China
- LY19H19003/Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China
- 2023R037/Zhejiang Province Traditional Medical Scientific Research Foundation
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
