NeuroMotion smartphone application for remote General Movements Assessment: a feasibility study in Nepal
- PMID: 38431302
- PMCID: PMC10910581
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2023-080063
NeuroMotion smartphone application for remote General Movements Assessment: a feasibility study in Nepal
Abstract
Objectives: To evaluate the feasibility of using the NeuroMotion smartphone application for remote General Movements Assessment for screening infants for cerebral palsy in Kathmandu, Nepal.
Method: Thirty-one term-born infants at risk of cerebral palsy due to birth asphyxia or neonatal seizures were recruited for the follow-up at Paropakar Maternity and Women's Hospital, 1 October 2021 to 7 January 2022. Parents filmed their children at home using the application at 3 months' age and the videos were assessed for technical quality using a standardised form and for fidgety movements by Prechtl's General Movements Assessment. The usability of the application was evaluated through a parental survey.
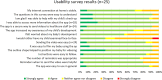
Results: Twenty families sent in altogether 46 videos out of which 35 had approved technical quality. Sixteen children had at least one video with approved technical quality. Three infants lacked fidgety movements. The level of agreement between assessors was acceptable (Krippendorf alpha 0.781). Parental answers to the usability survey were in general positive.
Interpretation: Engaging parents in screening of cerebral palsy with the help of a smartphone-aided remote General Movements Assessment is possible in the urban area of a South Asian lower middle-income country.
Keywords: Developmental neurology & neurodisability; Feasibility Studies; Follow-Up Studies; NEONATOLOGY; Nepal; eHealth.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2024. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: KS and HEKS developed the application NeuroMotion with financial support from a private donation through Knut och Alice Wallenbergs Stiftelse. For the purpose of further research and later implementation of NeuroMotion, the company NeuroMotion AB was founded and is the owner of the application. NeuroMotion AB is owned by KS and HEKS and has the purpose of research and to be non-profitable.
Figures

References
-
- World Health Organization . Nurturing care for early childhood development: a framework for helping children survive and thrive to transform health and human potential. World Health Organization, United Nations Children’s Fund, World Bank Group, 2018.
-
- Toldo M, Varishthananda S, Einspieler C, et al. . Enhancing early detection of neurological and developmental disorders and provision of intervention in low-resource settings in Uttar Pradesh, India: study protocol of the G.A.N.E.S.H. programme. BMJ Open 2020;10:e037335. 10.1136/bmjopen-2020-037335 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Benfer KA, Novak I, Morgan C, et al. . Community-based parent-delivered early detection and intervention programme for infants at high risk of cerebral palsy in a low-resource country (learning through everyday activities with parents (LEAP-CP): protocol for a randomised controlled trial. BMJ Open 2018;8:e021186. 10.1136/bmjopen-2017-021186 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
