RAB22A as a predictor of exosome secretion in the progression and relapse of multiple myeloma
- PMID: 38431306
- PMCID: PMC10968671
- DOI: 10.18632/aging.205565
RAB22A as a predictor of exosome secretion in the progression and relapse of multiple myeloma
Abstract
Background: Multiple myeloma (MM) is an incurable malignant plasma cell disease. We explored the role of RAB22A in exosome secretion, epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) and immune regulation.
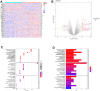
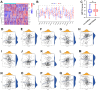
Methods: We obtained MM samples from Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) data sets. We downloaded the "IOBR" package, and used the "PCA" and "ssGSEA" algorithms to calculate the EMT scores and exosome scores. The "CIBERSORT" package was used to analyze the infiltration of immune cells. We extracted the exosomes of mesenchymal stem cell (MSC) to verify the biological function of RAB22A.
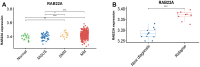
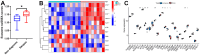
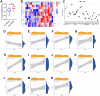
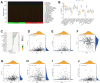
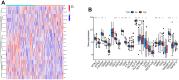
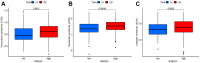
Results: The expression level of RAB22A in smoldering multiple myeloma (SMM) and MM patients was significantly higher than that in normal people and monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance (MGUS) patients, and the expression level of RAB22A in relapse MM patients was significantly higher than that in newly diagnosed patients. The EMT scores and exosome scores of high RAB22A group were significantly higher than those of low RAB22A group, and the exosome scores of MSC in recurrent patients were significantly higher than those of newly diagnosed patients. In addition, the infiltration levels of monocyte, NK cells resting, eosinophils, T cells regulatory and T cells CD4 memory activated were positively correlated with RAB22A. After down-regulating the expression of RAB22A in MM-MSC, the secretion of exosomes decreased. Compared with the exosomes of MSC in si-RAB22A group, the exosomes in control group significantly promoted the proliferation of MM.
Conclusions: RAB22A is a potential therapeutic target to improve the prognosis of MM, which is closely related to exosome secretion, EMT and immune cell infiltration.
Keywords: EMT; RAB22A; exosome secretion; immune regulation; multiple myeloma.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Regulation of RAB22A by mir-193b inhibits breast cancer growth and metastasis mediated by exosomes.Int J Oncol. 2018 Dec;53(6):2705-2714. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2018.4571. Epub 2018 Sep 25. Int J Oncol. 2018. PMID: 30272274
-
Bone marrow fibroblasts overexpress miR-27b and miR-214 in step with multiple myeloma progression, dependent on tumour cell-derived exosomes.J Pathol. 2019 Feb;247(2):241-253. doi: 10.1002/path.5187. J Pathol. 2019. PMID: 30357841
-
Monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance and smoldering multiple myeloma.Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 2014 Oct;28(5):775-90. doi: 10.1016/j.hoc.2014.06.005. Epub 2014 Jul 22. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 2014. PMID: 25212882 Review.
-
Addition of Rice Bran Arabinoxylan to Curcumin Therapy May Be of Benefit to Patients With Early-Stage B-Cell Lymphoid Malignancies (Monoclonal Gammopathy of Undetermined Significance, Smoldering Multiple Myeloma, or Stage 0/1 Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia): A Preliminary Clinical Study.Integr Cancer Ther. 2016 Jun;15(2):183-9. doi: 10.1177/1534735416635742. Epub 2016 May 6. Integr Cancer Ther. 2016. PMID: 27154182 Free PMC article.
-
Management of monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance (MGUS) and smoldering multiple myeloma (SMM).Oncology (Williston Park). 2011 Jun;25(7):578-86. Oncology (Williston Park). 2011. PMID: 21888255 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Mechanistic Insights into Tumorigenesis from Serum Proteins.medRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Jun 5:2025.06.04.25328977. doi: 10.1101/2025.06.04.25328977. medRxiv. 2025. PMID: 40502580 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Mapping Small Extracellular Vesicle Secretion Potential in Healthy Human Gingiva Using Spatial Transcriptomics.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2025 Apr 7;47(4):256. doi: 10.3390/cimb47040256. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2025. PMID: 40699655 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Landgren O, Kyle RA, Pfeiffer RM, Katzmann JA, Caporaso NE, Hayes RB, Dispenzieri A, Kumar S, Clark RJ, Baris D, Hoover R, Rajkumar SV. Monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance (MGUS) consistently precedes multiple myeloma: a prospective study. Blood. 2009; 113:5412–7. 10.1182/blood-2008-12-194241 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

