Finite element analysis of 3 internal fixations for distal type C3 femur fractures with medial wall bone defects
- PMID: 38432862
- PMCID: PMC10929944
- DOI: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7347.2023.230221
Finite element analysis of 3 internal fixations for distal type C3 femur fractures with medial wall bone defects
Abstract
Objectives: Managing 33-C3 femur fractures with medial wall bone defects poses a significant challenge for orthopedic surgeons. The gold standard treatment for arbeitsgemeinschaftfür osteosynthesefragen (AO)/orthopedic trauma association (OTA) 33-C3 distal femur fractures with medial wall bone defects remains elusive. This study employs finite element analysis to compare the stability and mechanical behavior of 3 internal fixation patterns (single lateral distal locking plate, retrograde intramedullary nail, and dual plates) for 33-C3 femur fractures with medial wall bone defects. The aim is to provide a theoretical basis for the selection of internal fixation modalities in clinical practice.
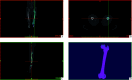
Methods: Enrollment included a 43-year-old male volunteer weighing 60 kg, without a history of femur fracture. Bilateral femur normality was verified through X-ray and CT scan assessments. A finite element simulation model of AO/OTA 33-C3 distal femur fracture with medial wall bone defect was established. Three fixation methods, named single lateral locking plate (single-plate group), retrograde intramedullary nail (retrograde intramedullary nail group), and dual plates (dual-plate group), were evaluated using finite element analysis under an axial load of 300 N. The assessment included an examination of von Mises stress distribution, shear stress, and displacement patterns at the internal fixation and femur fracture sites.
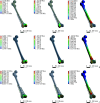
Results: The finite element analysis revealed that dual-plate fixation effectively reduced the concentration of von Mises stress at the plate on the fracture site. Under full weight-bearing conditions, the maximum von Mises stress in the implants occurred at the distal femur defect level, with values of 149.30, 59.281, and 58.03 MPa for single-plate fixation, retrograde intramedullary nail, and dual-plate fixation methods, respectively. Similarly, the maximum shear stress in the implants was 77.867, 30.136, and 33.505 MPa for single-plate fixation, retrograde intramedullary nail, and dual-plate fixation methods, respectively, all presenting at the distal femur defect level. The maximum relative displacements of implants during compressive loading were 1.34, 1.25, and 0.83 mm for the single-plate , retrograde intramedullary nail, and dual-plate groups, respectively. Consistently, the maximum loading-point displacements of fracture sites were 1.529, 1.264, and 0.880 mm for the single-plate fixation group, retrograde intramedullary nail group, and dual-plate fixation group, respectively. Furthermore, at the distal femur defect level, the maximum von Mises stress was 72.682, 112.430, and 40.716 MPa for the single-plate, retrograde intramedullary nail, and dual-plate fixation groups, respectively.
Conclusions: Dual-plate fixation demonstrates superior biomechanical outcomes and exhibites the lowest maximum von Mises stress and shear stress, along with minimal relative movements between fracture fragments. This configuration offers optimal mechanical stability for managing AO/OTA 33-C3 distal femur fractures with medial wall bone defects. Consequently, dual-plate fixation emerges as a better treatment strategy for patients presenting with comminuted intra-articular distal femur fractures accompanied by medial wall bone defects.
目的: 伴有内侧骨缺损的股骨远端C3型骨折预后差,目前尚无治疗伴有内侧骨缺损的股骨远端C3型骨折的金标准。本研究采用有限元分析比较股骨远端外侧单钢板、逆行髓内钉和内外侧双钢板这3种治疗伴有内侧骨缺损的股骨远端C3型骨折的内固定方式的生物力学特点,旨在为临床选择内固定治疗方式提供理论依据。方法: 选取1位43岁体重60 kg男性志愿者,无股骨骨折及骨病史,股骨X线及CT检测表明骨质条件无异常。运用螺旋CT对志愿者的股骨全长进行层厚1 mm的断层扫描,通过有限元分析方法基于CT采集数据建立伴有内侧骨缺损的股骨远端C3型骨折仿真模型,并分别建立股骨远端外侧解剖钢板(单钢板组)、逆行髓内钉(逆行髓内钉组)以及内外侧双钢板(双钢板组)固定的三维模型。模拟60 kg体重男性行走步态中单足负重中立位受力情况,对装配模型施加300 N轴向应力,观察各组模型中内植物的应力、剪切力、位移、股骨应力分布及骨折端位移情况。结果: 单钢板组、逆行髓内钉组、双钢板组的内植物应力峰值分别为149.300、59.281、58.038 MPa,应力峰值均在股骨远端骨缺损部位。单钢板组、逆行髓内钉组、双钢板组的内植物剪切力峰值分别为77.867、30.136、33.505 MPa,均出现在股骨远端骨缺损部位。单钢板组、逆行髓内钉组、双钢板组的内植物位移峰值分别为1.34、1.25、0.83 mm,骨折端位移峰值分别为1.529、1.264、0.880 mm,股骨应力峰值分别为72.682、112.430、40.716 MPa。结论: 在治疗伴有内侧骨缺损的股骨远端C3型骨折的3种模型中,双钢板组的内植物位移及应力峰值最小,股骨应力峰值最小,出现内固定断裂风险最低,可能是治疗伴有内侧骨缺损的股骨远端C3型骨折的更好选择。.
Keywords: comminuted intra-articular distal femur fracture; dual plate fixation; finite element analysis; medial wall bone defect.
Conflict of interest statement
作者声称无任何利益冲突。
Figures

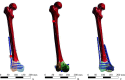




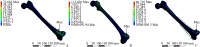

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

