Severe Anemia from Multiple Gastric Hyperplastic Polyps in a Hemodialysis Patient after Long-term Use of a Proton-pump Inhibitor
- PMID: 38432892
- PMCID: PMC10982011
- DOI: 10.2169/internalmedicine.2091-23
Severe Anemia from Multiple Gastric Hyperplastic Polyps in a Hemodialysis Patient after Long-term Use of a Proton-pump Inhibitor
Abstract
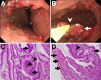
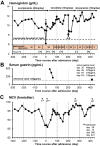
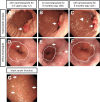
A 90-year-old man on maintenance hemodialysis was admitted due to severe symptomatic anemia. Biopsies under esophagogastroduodenoscopy demonstrated that the cause of anemia was intermittent blood oozing from multiple gastric hyperplastic polyps. Even after successful eradication of Helicobacter pylori, he showed hypergastrinemia (480 pg/mL) owing to esomeprazole (proton-pump inhibitor) therapy for the past 4.5 years to treat reflux esophagitis. Seven months after we switched esomeprazole to famotidine (H2-receptor antagonist), those gastric polyps and anemia were remarkably ameliorated with lowered gastrin levels. This case indicates that long-term use of a proton-pump inhibitor triggers chronic hypergastrinemia, leading to gastric hyperplastic polyps and subsequent severe anemia.
Keywords: gastric bleeding; gastric hyperplastic polyp; gastrin; hemodialysis; proton-pump inhibitor; severe anemia.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Adenocarcinoma arising in multiple hyperplastic polyps in a patient with Helicobacter pylori infection and hypergastrinemia during long-term proton pump inhibitor therapy.Clin J Gastroenterol. 2017 Apr;10(2):128-136. doi: 10.1007/s12328-017-0714-7. Epub 2017 Feb 3. Clin J Gastroenterol. 2017. PMID: 28160247
-
Proton Pump Inhibitor Associated Multiple Gastric Hyperplastic Polyps With Uncontrollable Bleeding: A Case Report.In Vivo. 2024 May-Jun;38(3):1465-1469. doi: 10.21873/invivo.13592. In Vivo. 2024. PMID: 38688629 Free PMC article.
-
Gastric Hyperplastic Polyps Associated with Proton Pump Inhibitor Use in a Case without a History of Helicobacter pylori Infection.Intern Med. 2017;56(14):1825-1829. doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.56.8040. Epub 2017 Jul 15. Intern Med. 2017. PMID: 28717077 Free PMC article.
-
Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) may cause gastric cancer - clinical consequences.Scand J Gastroenterol. 2018 Jun;53(6):639-642. doi: 10.1080/00365521.2018.1450442. Epub 2018 May 31. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2018. PMID: 29852782 Review.
-
Gastric cancer and gastrin: on the interaction of Helicobacter pylori gastritis and acid inhibitory induced hypergastrinemia.Scand J Gastroenterol. 2019 Sep;54(9):1118-1123. doi: 10.1080/00365521.2019.1663446. Epub 2019 Sep 14. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2019. PMID: 31524029 Review.
Cited by
-
Evaluating the detection rate and pathological features of polyps in patients with upper gastrointestinal endoscopy.World J Gastrointest Endosc. 2025 May 16;17(5):105471. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v17.i5.105471. World J Gastrointest Endosc. 2025. PMID: 40438721 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kalantar-Zadeh K, Jafar TH, Nitsch D, Neuen B, Perkovic V. Chronic kidney disease. Lancet 398: 786-802, 2021. - PubMed
-
- Jha V, Garcia-Garcia G, Iseki K, et al. . Chronic kidney disease: global dimension and perspectives. Lancet 382: 260-272, 2013. - PubMed
-
- Anderson S, Halter JB, Hazzard WR, et al. . Prediction, progression, and outcomes of chronic kidney disease in older adults. J Am Soc Nephrol 20: 1199-1209, 2009. - PubMed
-
- Nitta K, Goto S, Masakane N, et al. . Annual dialysis date report for 2018, JSDT Renal Data Registry: survey methods, facility data, incidence, prevalence, and mortality. Ren Replace Ther 6: 41, 2020.
-
- Macdougall IC, White C, Anker SD, et al. . Intravenous iron in patients undergoing maintenance hemodialysis. N Engl J Med 380: 447-458, 2019. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

