In silico evaluation of a new compound incorporating 4(3H)-quinazolinone and sulfonamide as a potential inhibitor of a human carbonic anhydrase
- PMID: 38433188
- PMCID: PMC10910740
- DOI: 10.1186/s13065-024-01150-1
In silico evaluation of a new compound incorporating 4(3H)-quinazolinone and sulfonamide as a potential inhibitor of a human carbonic anhydrase
Abstract
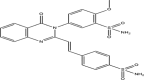
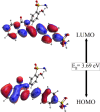
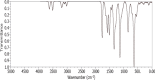
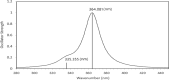
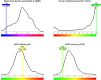
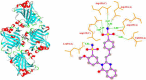
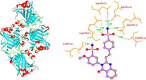
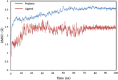
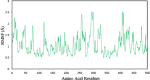
The present study investigates the potential of a new compound containing sulfonamide and 4(3H)-quinazolinone to inhibit the hCA-IIX enzyme using in silico methods. Density functional theory-based calculations of electronic properties have been addressed through the analysis of frontier molecular orbitals, molecule electrostatic potential, and IR and UV-vis spectroscopy data. A molecular electrostatic potential analysis predicts that the target protein will be most inhibited by the sulfonamide groups since it has the highest potential spots for electrophile and nucleophile attack. The investigated compound exhibited good ADMET properties and satisfied the Lipinski rule of drug likeness. The hCA-IIX protein binding affinity with the proposed compound was determined by molecular docking analysis, which revealed a stable conformation with more negative binding energy (-12.19 kcal/mol) than the standard AZA drug (-7.36 kcal/mol). Moreover, a molecular dynamics study confirmed the docking results through trajectory analysis. The RMSD and RMSF both showed convergence and no significant fluctuations during the simulation time, which revealed a stable interaction within the active domain of the target protein. According to these findings, the proposed compound has a good pharmacological nature and could potentially be an efficient drug against hCAIX enzymes.
Keywords: 2, 4(3H)-quinazolinone; ADMET; DFT; IR; Molecular docking; Molecular dynamics; Sulfonamide; UV–vis spectra.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A novel imidazole-based azo molecule: synthesis, characterization, quantum chemical calculations, molecular docking, molecular dynamics simulations and ADMET properties.J Mol Model. 2023 Jul 5;29(8):226. doi: 10.1007/s00894-023-05625-1. J Mol Model. 2023. PMID: 37405575
-
Computational discovery of plant-based inhibitors against human carbonic anhydrase IX and molecular dynamics simulation.J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2021 May;39(8):2754-2770. doi: 10.1080/07391102.2020.1753579. Epub 2020 Apr 29. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2021. PMID: 32266872
-
Investigation of the New Inhibitors by Sulfadiazine and Modified Derivatives of α-D-glucopyranoside for White Spot Syndrome Virus Disease of Shrimp by In Silico: Quantum Calculations, Molecular Docking, ADMET and Molecular Dynamics Study.Molecules. 2022 Jun 8;27(12):3694. doi: 10.3390/molecules27123694. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35744817 Free PMC article.
-
Design, Synthesis, Kinetic Analysis and Pharmacophore-Directed Discovery of 3-Ethylaniline Hybrid Imino-Thiazolidinone as Potential Inhibitor of Carbonic Anhydrase II: An Emerging Biological Target for Treatment of Cancer.Biomolecules. 2022 Nov 16;12(11):1696. doi: 10.3390/biom12111696. Biomolecules. 2022. PMID: 36421710 Free PMC article.
-
Thermodynamic, kinetic, and structural parameterization of human carbonic anhydrase interactions toward enhanced inhibitor design.Q Rev Biophys. 2018 Jan;51:e10. doi: 10.1017/S0033583518000082. Q Rev Biophys. 2018. PMID: 30912486 Review.
References
-
- Syrjänen L, Tolvanen M, Hilvo M, Olatubosun A, Innocenti A, Scozzafava A, et al. Characterization of the first beta-class carbonic anhydrase from an arthropod (Drosophila melanogaster) and phylogenetic analysis of beta-class carbonic anhydrases in invertebrates. BMC Biochem. 2010;11:28. doi: 10.1186/1471-2091-11-28. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Nerella SG, Thacker PS, Arifuddin M, Supuran CT. Tumor associated carbonic anhydrase inhibitors: rational approaches, design strategies, structure activity relationship and mechanistic insights. Eur J Med Chem Rep. 2024;10:100131.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
