Keratinocyte-derived circulating microRNAs in extracellular vesicles: a novel biomarker of psoriasis severity and potential therapeutic target
- PMID: 38433211
- PMCID: PMC10910723
- DOI: 10.1186/s12967-024-05030-z
Keratinocyte-derived circulating microRNAs in extracellular vesicles: a novel biomarker of psoriasis severity and potential therapeutic target
Abstract
Background: Psoriasis is a chronic inflammatory disorder characterized by pathogenic hyperproliferation of keratinocytes and immune dysregulation. Currently, objective evaluation tools reflecting the severity of psoriasis are insufficient. MicroRNAs in extracellular vesicles (EV miRNAs) have been shown to be potential biomarkers for various inflammatory diseases. Our objective was to investigate the possibility of plasma-derived EV miRNAs as a marker for the psoriasis disease severity.
Methods: EVs were extracted from the plasma of 63 patients with psoriasis and 12 with Behçet's disease. We performed next-generation sequencing of the plasma-derived EV miRNAs from the psoriasis patients. Real-time quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) was used to validate the level of EV miRNA expression. In situ hybridization was used to discern the anatomical location of miRNAs. qRT-PCR, western blotting, and cell counting kits (CCKs) were used to investigate IGF-1 signaling in cells transfected with miRNA mimics.
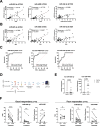
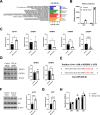
Results: We identified 19 differentially expressed EV miRNAs and validated the top three up-and down-regulated EV miRNAs. Among these, miR-625-3p was significantly increased in patients with severe psoriasis in both plasma and skin and most accurately distinguished moderate-to-severe psoriasis from mild-to-moderate psoriasis. It was produced and secreted by keratinocytes upon stimulation. We also observed a significant intensification of IGF-1 signalling and increased cell numbers in the miR-625-3p mimic transfected cells.
Conclusions: We propose keratinocyte-derived EV miR-625-3p as a novel and reliable biomarker for estimating the severity of psoriasis. This biomarker could objectively evaluate the severity of psoriasis in the clinical setting and might serve as a potential therapeutic target. Trial registration None.
Keywords: Biomarkers; Extracellular vesicles; Keratinocytes; Psoriasis; miR-625-3p; microRNAs.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
No competing interests.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

