The role of kinesin family members in hepatobiliary carcinomas: from bench to bedside
- PMID: 38433242
- PMCID: PMC10910842
- DOI: 10.1186/s40364-024-00559-z
The role of kinesin family members in hepatobiliary carcinomas: from bench to bedside
Abstract
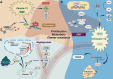
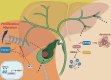
As a major component of the digestive system malignancies, tumors originating from the hepatic and biliary ducts seriously endanger public health. The kinesins (KIFs) are molecular motors that enable the microtubule-dependent intracellular trafficking necessary for mitosis and meiosis. Normally, the stability of KIFs is essential to maintain cell proliferation and genetic homeostasis. However, aberrant KIFs activity may destroy this dynamic stability, leading to uncontrolled cell division and tumor initiation. In this work, we have made an integral summarization of the specific roles of KIFs in hepatocellular and biliary duct carcinogenesis, referring to aberrant signal transduction and the potential for prognostic evaluation. Additionally, current clinical applications of KIFs-targeted inhibitors have also been discussed, including their efficacy advantages, relationship with drug sensitivity or resistance, the feasibility of combination chemotherapy or other targeted agents, as well as the corresponding clinical trials. In conclusion, the abnormally activated KIFs participate in the regulation of tumor progression via a diverse range of mechanisms and are closely associated with tumor prognosis. Meanwhile, KIFs-aimed inhibitors also carry out a promising tumor-targeted therapeutic strategy that deserves to be further investigated in hepatobiliary carcinoma (HBC).
Keywords: Hepatobiliary carcinoma; Kinesin; Prognosis assessment; Signaling transduction; Targeted therapy.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

