Heterozygous THBS2 pathogenic variant causes Ehlers-Danlos syndrome with prominent vascular features in humans and mice
- PMID: 38433265
- PMCID: PMC11061164
- DOI: 10.1038/s41431-024-01559-1
Heterozygous THBS2 pathogenic variant causes Ehlers-Danlos syndrome with prominent vascular features in humans and mice
Abstract
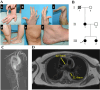
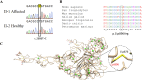
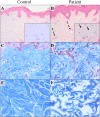
Ehlers-Danlos syndromes (EDS) are a group of connective tissue disorders caused by mutations in collagen and collagen-interacting genes. We delineate a novel form of EDS with vascular features through clinical and histopathological phenotyping and genetic studies of a three-generation pedigree, displaying an apparently autosomal dominant phenotype of joint hypermobility and frequent joint dislocations, atrophic scarring, prolonged bleeding time and age-related aortic dilatation and rupture. Coagulation tests as well as platelet counts and function were normal. Reticular dermis displayed highly disorganized collagen fibers and transmission electron microscopy (TEM) revealed abnormally shaped fibroblasts and endothelial cells, with high amount and irregular shape of extracellular matrix (ECM) substance, especially near blood vessels. Genetic analysis unraveled a heterozygous mutation in THBS2 (NM_003247.5:c.2686T>C, p.Cys896Arg). We generated CRISPR/Cas9 knock-in (KI) mice, bearing the heterozygous human mutation in the mouse ortholog. The KI mice demonstrated phenotypic traits correlating with those observed in the human subjects, as evidenced by morphologic, histologic, and TEM analyses, in conjunction with bleeding time assays. Our findings delineate a novel form of human EDS with classical-like elements combined with vascular features, caused by a heterozygous THBS2 missense mutation. We further demonstrate a similar phenotype in heterozygous THBS2Cys896Arg KI mice, in line with previous studies in Thbs2 homozygous null-mutant mice. Notably, THBS2 encodes Thrombospondin-2, a secreted homotrimeric matricellular protein that directly binds the ECM-shaping Matrix Metalloproteinase 2 (MMP2), mediating its clearance. THBS2 loss-of-function attenuates MMP2 clearance, enhancing MMP2-mediated proteoglycan cleavage, causing ECM abnormalities similar to those seen in the human and mouse disease we describe.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Homozygous Gly530Ser substitution in COL5A1 causes mild classical Ehlers-Danlos syndrome.Am J Med Genet. 2002 May 15;109(4):284-90. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.10373. Am J Med Genet. 2002. PMID: 11992482
-
Haploinsufficiency of the murine Col3a1 locus causes aortic dissection: a novel model of the vascular type of Ehlers-Danlos syndrome.Cardiovasc Res. 2011 Apr 1;90(1):182-90. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvq356. Epub 2010 Nov 10. Cardiovasc Res. 2011. PMID: 21071432 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical and Molecular Characterization of Classical-Like Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome Due to a Novel TNXB Variant.Genes (Basel). 2019 Oct 25;10(11):843. doi: 10.3390/genes10110843. Genes (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31731524 Free PMC article.
-
Pathogenic mechanisms in genetically defined Ehlers-Danlos syndromes.Trends Mol Med. 2024 Sep;30(9):824-843. doi: 10.1016/j.molmed.2024.06.001. Epub 2024 Aug 14. Trends Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 39147618 Review.
-
Genetic heterogeneity and clinical variability in musculocontractural Ehlers-Danlos syndrome caused by impaired dermatan sulfate biosynthesis.Hum Mutat. 2015 May;36(5):535-47. doi: 10.1002/humu.22774. Epub 2015 Apr 6. Hum Mutat. 2015. PMID: 25703627 Review.
Cited by
-
VARista: a free web platform for streamlined whole-genome variant analysis across T2T, hg38, and hg19.Hum Genet. 2024 May;143(5):695-701. doi: 10.1007/s00439-024-02671-4. Epub 2024 Apr 12. Hum Genet. 2024. PMID: 38607411
-
Novel insights into cancer predisposition genes.Eur J Hum Genet. 2024 May;32(5):469-470. doi: 10.1038/s41431-024-01620-z. Eur J Hum Genet. 2024. PMID: 38688979 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
GeniePool 2.0: advancing variant analysis through CHM13-T2T, AlphaMissense, gnomAD V4 integration, and variant co-occurrence queries.Database (Oxford). 2024 Dec 27;2024:baae130. doi: 10.1093/database/baae130. Database (Oxford). 2024. PMID: 39729312 Free PMC article.
-
Shaping the future of care for patients with Ehlers-Danlos syndromes: from multidisciplinary management to precision medicine.Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2025 Mar 3;20(1):98. doi: 10.1186/s13023-025-03615-5. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2025. PMID: 40033344 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Selecting the Substantially Touched Vertebra as the Lowest Instrumented Vertebra in Spinal Surgeries for B3GALT6 -Related Disorders: Clinical Experience and Literature Review.Orthop Surg. 2025 Jul;17(7):2025-2037. doi: 10.1111/os.70072. Epub 2025 May 15. Orthop Surg. 2025. PMID: 40371684 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Blackburn PR, Xu Z, Tumelty KE, Zhao RW, Monis WJ, Harris KG, et al. Bi-allelic Alterations in AEBP1 Lead to Defective Collagen Assembly and Connective Tissue Structure Resulting in a Variant of Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome. Am J Hum Genet. 2018;102:696–705. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2018.02.018. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

