Evaluation of the modified 3Mix-Simvastatin combination in non-instrumental endodontic therapy of necrotic primary molars: A two-arm randomized controlled trial
- PMID: 38433296
- PMCID: PMC10909793
- DOI: 10.1002/cre2.860
Evaluation of the modified 3Mix-Simvastatin combination in non-instrumental endodontic therapy of necrotic primary molars: A two-arm randomized controlled trial
Abstract
Objective: This study aimed to assess the clinical and radiographic outcomes of non-instrumentation endodontic treatment (NIET) using a modified antibiotic mix of cefixime, ciprofloxacin and metronidazole with simvastatin (an anti-inflammatory, bone regeneration drug) on necrotic primary molars compared to conventional pulpectomy to help preservation of necrotic primary teeth until its natural exfoliation.
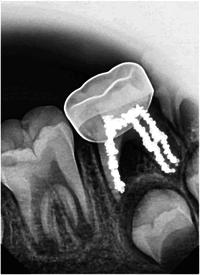
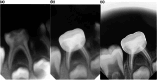
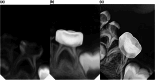
Materials and methods: Forty mandibular primary second molars with necrotic pulp tissue from 38 healthy patients aged between 4 and 8 years were randomly assigned to two groups with a 1:1 allocation ratio. Group A teeth underwent conventional root canal treatment. The procedure involved a two-visit approach, employing k-files and h-files during the initial visit, followed by the application of calcium hydroxide paste as canal dressing between visits, while Group B teeth were treated with 3Mixtatin. All teeth were clinically evaluated after 1, 3, 6, and 12 months, and radiographically at 3, 6, and 12 months. Two external examiners assessed the results. Data analysis was conducted using a chi-square test at a 0.05 significance level.
Results: At the end of the follow-up interval, 90% of teeth in each group exhibited no clinical signs or symptoms. Additionally, inter-radicular radiolucency healing occurred in 75% of cases in the NIET group and 89.5% in the conventional pulpectomy group. However, no statistically significant difference was found between the two groups.
Conclusion: NIET using 3Mixtatin seems to be a good alternative choice to conventional pulpectomy, offering a less complex treatment approach that may help avoid the complications associated with traditional pulpectomy and could be suitable for teeth with shorter roots.
Keywords: dental pulp necrosis; lesion sterilization and tissue repair; pulpectomy; root canal therapy.
© 2024 The Authors. Clinical and Experimental Dental Research published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Aminabadi, N. , Huang, B. , Samiei, M. , Agheli, S. , Jamali, Z. , & Shirazi, S. (2016). A randomized trial using 3Mixtatin compared to MTA in primary molars with inflammatory root resorption: A novel endodontic biomaterial. Journal of Clinical Pediatric Dentistry, 40(2), 95–102. 10.17796/1053-4628-40.2.95 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Aminabadi, N. A. , Maljaei, E. , Erfanparast, L. , Aghbali, A. A. , Hamishehkar, H. , & Najafpour, E. (2013). Simvastatin versus calcium hydroxide direct pulp capping of human primary molars: A randomized clinical trial. Journal of Dental Research, Dental Clinics, Dental Prospects, 7(1), 8. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Anila, B. , Murali, H. , Cheranjeevi, J. , & Kapil, R. (2020). Lesion sterilization and tissue repair (LSTR): A review. Journal of Scientific Dentistry, 4(2), 49–55.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

