Embitterment in Vietnam War Veterans Predicted by Symptoms of Posttraumatic Stress Disorder
- PMID: 38433418
- PMCID: PMC10910164
- DOI: 10.30773/pi.2023.0299
Embitterment in Vietnam War Veterans Predicted by Symptoms of Posttraumatic Stress Disorder
Abstract
Objective: Research on the association between posttraumatic embitterment disorder (PTED) and other psychopathologies in veterans and adults aged ≥65 years is lacking. This study aimed to assess embitterment among elderly war veterans and its association with major psychopathological factors.
Methods: Participants included Vietnam War veterans who visited a psychiatric clinic. Based on the Posttraumatic Embitterment Disorder Self-Rating Scale (PTEDS) score, the participants were divided into the embitterment (PTED(+), mean score of PTEDS items [mPTEDS] ≥1.6) and non-embitterment (PTED(-), mPTEDS <1.6) groups. Demographic characteristics, combat exposure severity, depression, anxiety, sleep, and alcohol use disorder symptom scores of the participants were collected and compared between the PTED(+) and PTED(-) groups. A correlation analysis between symptom measure scores and the mPTEDS was conducted. The influence of psychopathology on embitterment was investigated using stepwise multiple linear regression analysis.
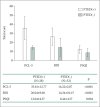
Results: In total, 60 participants (28 in PTED(+) and 32 in PTED(-)) were included. Among those in PTED(+), 21 (35.0%) showed mild embitterment symptoms (1.6≤ mPTEDS <2.5) and 7 (11.7%) reported moderate or severe embitterment symptoms (mPTEDS ≥2.5). The mean scores of posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD), depression, and anxiety were significantly higher in the PTED(+) than in the PTED(-) group. The mPTEDS were significantly correlated with PTSD, depression, anxiety, and sleep disorder scores. The PTSD symptoms significantly explained the higher mPTEDS score in a regression model.
Conclusion: Embitterment symptoms were associated with PTSD, depression, anxiety, and insomnia symptoms in elderly veterans, similar to the results of prior studies involving only the general population.
Keywords: Adjustment disorders; Anxiety; Depression; Stress disorders, Post-traumatic; Veterans health.
Conflict of interest statement
Changsu Han, a contributing editor of the
Figures
References
-
- Linden M. Posttraumatic embitterment disorder. Psychother Psychosom. 2003;72:195–202. - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization . ICD-10: international statistical classification of diseases and related health problems. 10th revision, 2nd edition. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2004.
-
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic criteria and codes. In: American Psychiatric Association editor. Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders, fifth edition, text revision (DSM-TR). Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Association Publishing, 2022, p.32.
-
- American Psychiatric Association. Trauma- and stressor-related disorders. In: American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders, fifth edition, Text Revision (DSM-5-TR). Arlington: American Psychiatric Association Publishing; 2013, p.265.
-
- Linden M, Maercker A. Embitterment: societal, psychological, and clinical perspectives. Germany: Springer Science and Business Media; 2011.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

