Highly sensitive and simultaneous detection of ascorbic acid, dopamine, and uric acid using Pt@g-C3N4/N-CNTs nanocomposites
- PMID: 38433909
- PMCID: PMC10907839
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.109241
Highly sensitive and simultaneous detection of ascorbic acid, dopamine, and uric acid using Pt@g-C3N4/N-CNTs nanocomposites
Abstract
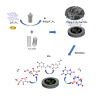
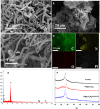
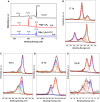
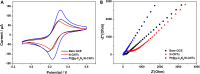
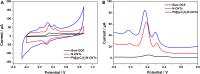
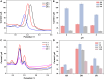
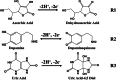
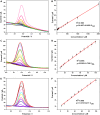
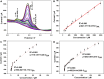
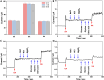
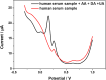
The detection of ascorbic acid (AA), dopamine (DA), and uric acid (UA) is crucial for understanding and managing various illnesses. In this research, Pt@g-C3N4 nanoparticles were synthesized via hydrothermal method and combined with N-doped carbon nanotubes (N-CNTs). The Pt@g-C3N4/N-CNTs-modified glassy carbon (GC) electrode was fabricated as an electrochemical sensor for the determination of AA, DA, and UA. The linear response range of AA, DA, and UA in the optimal condition was 100-3,000 μM, 1-100 μM, and 2-215 μM boasting a low detection limit (S/N = 3) of 29.44 μM (AA), 0.21 μM (UA), and 2.99 μM (DA), respectively. Additionally, the recoveries of AA, DA, and UA in serum sample were 100.4%-106.7%. These results corroborate the feasibility of the proposed method for the simultaneous, sensitive, and reliable detection of AA, DA, and UA. Our Pt@g-C3N4/N-CNTs/GC electrode can provide a potential strategy for disease diagnosis and health monitoring in clinical settings.
Keywords: Applied sciences; Electrochemistry; Nanomaterials; Sensor.
© 2024 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Ciobanu C.A., Ionita I., Mihailescu A.I., Ciobanu A.M. Cyclic voltammetry as a measuring tool in Parkinson’s disease and associated psychiatric commorbidities. Eur. Psychiatr. 2023;66:S757–S758. doi: 10.1192/j.eurpsy.2023.1597. - DOI
-
- Tzounakas V.L., Anastasiadi A.T., Arvaniti V.-Z., Lelli V., Fanelli G., Paronis E.C., Apostolidou A.C., Balafas E.G., Kostomitsopoulos N.G., Papageorgiou E.G., et al. Supplementation with uric and ascorbic acid protects stored red blood cells through enhancement of non-enzymatic antioxidant activity and metabolic rewiring. Redox Biol. 2022;57 doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2022.102477. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

