Light-responsive polymeric nanoparticles for retinal drug delivery: design cues, challenges and future perspectives
- PMID: 38434257
- PMCID: PMC10906429
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e26616
Light-responsive polymeric nanoparticles for retinal drug delivery: design cues, challenges and future perspectives
Abstract
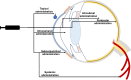
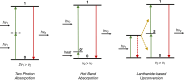
A multitude of sight-threatening retinal diseases, affecting hundreds of millions around the globe, lack effective pharmacological treatments due to ocular barriers and common drug delivery limitations. Polymeric nanoparticles (PNPs) are versatile drug carriers with sustained drug release profiles and tunable physicochemical properties which have been explored for ocular drug delivery to both anterior and posterior ocular tissues. PNPs can incorporate a wide range of drugs and overcome the challenges of conventional retinal drug delivery. Moreover, PNPs can be engineered to respond to specific stimuli such as ultraviolet, visible, or near-infrared light, and allow precise spatiotemporal control of the drug release, enabling tailored treatment regimens and reducing the number of required administrations. The objective of this study is to emphasize the therapeutic potential of light-triggered drug-loaded polymeric nanoparticles to treat retinal diseases through an exploration of ocular pathologies, challenges in drug delivery, current production methodologies and recent applications. Despite challenges, light-responsive PNPs hold the promise of substantially enhancing the treatment landscape for ocular diseases, aiming for an improved quality of life for patients.
Keywords: Light-triggered release; Ocular nanomedicine; Polymeric nanoparticles; Retinal diseases.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures





References
-
- Rodrigues F.S.C., Campos A., Martins J., Ambrósio A.F., Campos E.J. Emerging trends in nanomedicine for improving ocular drug delivery: light-responsive nanoparticles, mesoporous silica nanoparticles, and contact lenses. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2020;6:6587–6597. doi: 10.1021/acsbiomaterials.0c01347. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Nguyen D.D., Lai J.-Y. Advancing the stimuli response of polymer-based drug delivery systems for ocular disease treatment. Polym. Chem. 2020;11:6988–7008. doi: 10.1039/D0PY00919A. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

