Biomechanical study of different bone cement distribution on osteoporotic vertebral compression Fracture-A finite element analysis
- PMID: 38434291
- PMCID: PMC10907677
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e26726
Biomechanical study of different bone cement distribution on osteoporotic vertebral compression Fracture-A finite element analysis
Abstract
Purpose: This study aimed to compare the biomechanical effects of different bone cement distribution methods on osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures (OVCF).
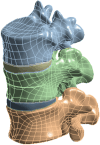
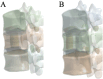
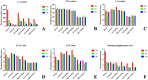
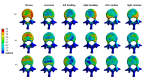
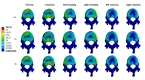
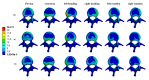
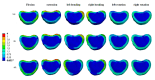
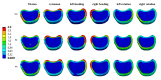
Patients and methods: Raw CT data from a healthy male volunteer was used to create a finite element model of the T12-L2 vertebra using finite element software. A compression fracture was simulated in the L1 vertebra, and two forms of bone cement dispersion (integration group, IG, and separation group, SG) were also simulated. Six types of loading (flexion, extension, left/right bending, and left/right rotation) were applied to the models, and the stress distribution in the vertebra and intervertebral discs was observed. Additionally, the maximum displacement of the L1 vertebra was evaluated.
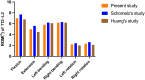
Results: Bone cement injection significantly reduced stress following L1 vertebral fractures. In the L1 vertebral body, the maximum stress of SG was lower than that of IG during flexion, left/right bending, and left/right rotation. In the T12 vertebral body, compared with IG, the maximum stress of SG decreased during flexion and right rotation. In the L2 vertebral body, the maximum stress of SG was the lowest under all loading conditions. In the T12-L1 intervertebral disc, compared with IG, the maximum stress of SG decreased during flexion, extension, and left/right bending and was basically the same during left/right rotation. However, in the L1-L2 intervertebral discs, the maximum stress of SG increased during left/right rotation compared with that of IG. Furthermore, the maximum displacement of SG was smaller than that of IG in the L1 vertebral bodies under all loading conditions.
Conclusions: SG can reduce the maximum stress in the vertebra and intervertebral discs, offering better biomechanical performance and improved stability than IG.
Keywords: Biomechanics; Bone cement distribution; Compression fracture; Finite element analysis; Osteoporosis; Vertebroplasty.
© 2024 Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
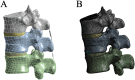


Similar articles
-
[Biomechanical effects of different bone cement diffusion patterns after vertebroplasty:finite element analysis].Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2021 Aug 25;34(8):732-7. doi: 10.12200/j.issn.1003-0034.2021.08.008. Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2021. PMID: 34423616 Chinese.
-
Biomechanical comparison between unilateral and bilateral percutaneous vertebroplasty for osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures: A finite element analysis.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022 Sep 8;10:978917. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2022.978917. eCollection 2022. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 36159704 Free PMC article.
-
Do we have to pursue complete reduction after PVA in osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures: a finite element analysis.Injury. 2022 Aug;53(8):2754-2762. doi: 10.1016/j.injury.2022.06.013. Epub 2022 Jun 12. Injury. 2022. PMID: 35760641
-
Finite element analysis of vertebroplasty in the osteoporotic T11-L1 vertebral body: Effects of bone cement formulation.J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2024 Jan;112(1):e35359. doi: 10.1002/jbm.b.35359. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2024. PMID: 38247244
-
Long-term effects of vertebroplasty: adjacent vertebral fractures.J Long Term Eff Med Implants. 2006;16(4):265-80. doi: 10.1615/jlongtermeffmedimplants.v16.i4.10. J Long Term Eff Med Implants. 2006. PMID: 17073569 Review.
Cited by
-
Biomechanical study between percutaneous vertebroplasty combined with cement pedicle plasty improves vertebral biomechanical stability: A finite element analysis.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2024 Jul 29;25(1):597. doi: 10.1186/s12891-024-07689-3. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2024. PMID: 39075431 Free PMC article.
-
Static study and numerical simulation of the influence of cement distribution in the upper and lower adjacent vertebrae on sandwich vertebrae in osteoporotic patients: Finite element analysis.JOR Spine. 2024 Jun 21;7(2):e1343. doi: 10.1002/jsp2.1343. eCollection 2024 Jun. JOR Spine. 2024. PMID: 38911099 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zhao G., Liu X., Li F. Balloon kyphoplasty versus percutaneous vertebroplasty for treatment of osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures (OVCFs) Osteoporos. Int. 2016;27(9):2823–2834. - PubMed
-
- Alsoof D., et al. Diagnosis and management of vertebral compression fracture. Am. J. Med. 2022;135(7):815–821. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

