The association between high mobility group box 1 (HMGB1) and Interleukin-18 (IL-18) serum concentrations in COVID-19 inpatients
- PMID: 38434314
- PMCID: PMC10907672
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e26619
The association between high mobility group box 1 (HMGB1) and Interleukin-18 (IL-18) serum concentrations in COVID-19 inpatients
Abstract
Background: High mobility group box 1 (HMGB1) and interleukin-18 (IL-18) are involved in various non-coronavirus disease pathogenesis and are reported as potential biomarkers for coronavirus disease (COVID-19). However, their association with COVID-19 pathogenesis has not yet been explored.
Aim: This study aimed to investigate the association between HMGB1 and IL-18 concentrations in the sera of COVID-19 patients versus non-COVID-19 patients.
Material and methods: We used stored serum samples obtained from 30 COVID-19 patients and 30 non-COVID-19 patients. We collected data on age, gender, treatment status, principal diagnosis, and comorbidity from patient medical records. HMGB1 and IL-18 concentrations were analyzed in the serum by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). The swab samples' RT-PCR cycle threshold (CT) values were obtained from the laboratory database.
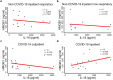
Results: HMGB1 concentrations were increased in the COVID-19 inpatients and non-COVID-19 inpatients compared to non-COVID-19 outpatients (COVID-19 inpatients vs. non-COVID-19 outpatients: 151.33 (90.27-192.38) vs. 80.75 (54.16-128.72) ng/ml; p = 0.0316; non-COVID-19 inpatients vs. non-COVID-19 outpatients: 152.66 (104.04-288.51) vs. 80.75 (54.16-128.72) ng/ml; p = 0.0199). IL-18 concentrations were also higher in the COVID-19 inpatients and non-COVID-19 inpatients compared to non-COVID-19 outpatients (COVID-19 inpatients vs. non-COVID-19 outpatients: 620.00 (461.50-849.6) vs. 403.10 (372.70-556.90) pg/ml; p = 0.0376; non-COVID-19 inpatients vs. non-COVID-19 outpatients: 835.70 (558.30-1602.00) vs. 403.10 (372.70-556.90) pg/ml; p = 0.0026). Moreover, HMGB1 was associated with IL-18 concentrations in the sera of COVID-19 inpatients (p = 0.0337; r = 0.5500).
Conclusion: The association of HMGB1 and IL-18 in COVID-19 might indicate the potential for a dangerous cycle leading to a cytokine storm to occur.
Keywords: COVID-19; HMGB1; IL-18; Inpatients; Non-COVID-19; Outpatients.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Impact of intestinal ischemia/reperfusion and lymph drainage on distant organs in rats.World J Gastroenterol. 2012 Dec 28;18(48):7271-8. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i48.7271. World J Gastroenterol. 2012. PMID: 23326132 Free PMC article.
-
[Expression of high mobility group box-1 in the lung tissue and serum of patients with pulmonary tuberculosis].Zhonghua Jie He He Hu Xi Za Zhi. 2013 Jul;36(7):497-500. Zhonghua Jie He He Hu Xi Za Zhi. 2013. PMID: 24262084 Chinese.
-
Association analysis of high-mobility group box-1 protein 1 (HMGB1)/toll-like receptor (TLR) 4 with nasal interleukins in allergic rhinitis patients.Cytokine. 2020 Feb;126:154880. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2019.154880. Epub 2019 Nov 15. Cytokine. 2020. PMID: 31739216
-
[Association between protective effect of Liuwei Wuling tablets against acute liver injury and its inhibitory effect on cytoplasmic translocation of high-mobility group box-1 in hepatocytes in mice].Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi. 2016 Feb;24(2):114-8. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1007-3418.2016.02.008. Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi. 2016. PMID: 26983478 Chinese.
-
[High mobility group box-1 protein activates endothelial cells to produce cytokines and has synergistic effect with lipopolysaccharide in inducing interleukin-6 release].Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2006 May 9;86(17):1191-5. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2006. PMID: 16796861 Chinese.
Cited by
-
Evaluation of inflammatory biomarkers and their association with anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibody titers in healthcare workers vaccinated with BNT162B2.Front Immunol. 2024 Aug 23;15:1447317. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1447317. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39247198 Free PMC article.
-
Tephrosia purpurea, with (-)-Pseudosemiglabrin as the Major Constituent, Alleviates Severe Acute Pancreatitis-Mediated Acute Lung Injury by Modulating HMGB1 and IL-22.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Mar 13;26(6):2572. doi: 10.3390/ijms26062572. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40141214 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Puno G.R., Puno R.C.C., Maghuyop I.V. COVID-19 case fatality rates across Southeast Asian countries (SEA): a preliminary estimate using a simple linear regression model. J Heal Res. 2020;35(3):286–294. doi: 10.1108/JHR-06-2020-0229. - DOI
-
- Unicef UNICEF . 2022. Indonesia COVID-19 Situation Report: October-December 2022-Indonesia|ReliefWeb.https://reliefweb.int/report/indonesia/unicef-indonesia-covid-19-situati...
-
- WHO . 2023. Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard with Vaccination Data; p. 1.https://covid19.who.int/
-
- CDC . CDC; 2023. Underlying Medical Conditions Associated with Higher Risk for Severe COVID-19: Information for Healthcare Professionals.https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/hcp/clinical-care/underlyingco...
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

