Efficacy and safety of Perampanel in the treatment of post stroke epilepsy: A multicenter, real-world study
- PMID: 38434369
- PMCID: PMC10907510
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e26376
Efficacy and safety of Perampanel in the treatment of post stroke epilepsy: A multicenter, real-world study
Abstract
Background: Since 2019, Perampanel (PER) has been endorsed in China as an adjunctive treatment for focal seizures, both with and without impaired awareness, and for the transition from focal to bilateral tonic-clonic seizures. Limited research exists regarding the efficacy of PER in treating post-stroke epilepsy (PSE) in China. Empirical studies are essential to guide treatment protocols. We conducted a retrospective study to assess the efficacy and tolerability of PER in 58 PSE patients treated between October 2019 and July 2023.
Method: This study encompassed 58 patients with PSE, treated with PER either as monotherapy or as part of adjunctive therapy, and underwent follow-up for a minimum duration of 6 months. The study assessed changes in seizure frequency, adverse events (AEs), drug retention rate, maintenance dose, and adverse reactions following PER treatment.
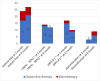
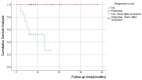
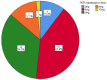
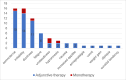
Results: The study included 58 PSE patients, with 60.3% males and 39.7% females, ranging in age from 18 to 89, mostly within the 61-70 age group. Ischemic strokes constituted 58.6% of cases, while hemorrhagic strokes accounted for 41.4%. Focal seizures, either with or without impaired awareness, were noted in 62.1% of patients, and a transition from focal to bilateral tonic-clonic seizures was seen in 32.8%. The retention rates for PER at 3 and 6 months stood at 94.8% and 84.5% respectively, and the most commonly administered maintenance dose was 4 mg/day (41.28%). In the adjunctive therapy group, efficacy rates were 66.7% at 3 months and 78.6% at 6 months, compared to 80.0% at 3 months and 85.7% at 6 months in the monotherapy group. In the efficacy analysis, with a criterion of ≥50% reduction in seizure frequency, the overall efficacy rates at 3 and 6 months were 69.1% and 79.6%, respectively. Adverse reactions occurred in 46.6% of patients, primarily involving irritability and somnolence (both 27.6%), with no marked difference in incidence between the adjunctive and monotherapy groups (P > 0.05).
Conclusion: PER exhibits favorable efficacy and tolerability in Chinese PSE patients, possibly at lower doses.
Keywords: Clinical efficacy; Perampanel; Post-stroke epilepsy; Safety.
© 2024 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Efficacy of perampanel by etiology in Japanese patients with epilepsy-subpopulation analysis of a prospective post-marketing observational study.Epilepsia Open. 2024 Oct;9(5):1772-1782. doi: 10.1002/epi4.13002. Epub 2024 Jul 4. Epilepsia Open. 2024. PMID: 38963336 Free PMC article.
-
Safety and effectiveness of perampanel monotherapy after adjunctive therapy through retention rate in subjects with focal-onset seizures with or without focal to bilateral tonic-clonic seizures: A multicenter retrospective study in Korea.Epilepsy Behav. 2023 Aug;145:109291. doi: 10.1016/j.yebeh.2023.109291. Epub 2023 Jun 17. Epilepsy Behav. 2023. PMID: 37336136
-
Efficacy and safety of perampanel monotherapy in Chinese patients with focal-onset seizures: A single-center, prospective, real-world observational study.Epilepsia Open. 2023 Dec;8(4):1474-1483. doi: 10.1002/epi4.12823. Epub 2023 Sep 25. Epilepsia Open. 2023. PMID: 37661647 Free PMC article.
-
Perampanel as monotherapy and adjunctive therapy for focal onset seizures, focal to bilateral tonic-clonic seizures and as adjunctive therapy of generalized onset tonic-clonic seizures.Expert Rev Neurother. 2019 Jan;19(1):5-16. doi: 10.1080/14737175.2019.1555474. Epub 2018 Dec 18. Expert Rev Neurother. 2019. PMID: 30560703 Review.
-
Perampanel monotherapy for the treatment of epilepsy: Clinical trial and real-world evidence.Epilepsy Behav. 2022 Nov;136:108885. doi: 10.1016/j.yebeh.2022.108885. Epub 2022 Sep 21. Epilepsy Behav. 2022. PMID: 36150304 Review.
References
-
- Yuan X., Fu Z., Ji P., Guo L., Al-Ghamdy A.O., Alkandiri A., Habotta O.A., Abdel Moneim A.E., Kassab R.B. Selenium nanoparticles pre-treatment reverse behavioral, oxidative damage, neuronal loss and neurochemical alterations in pentylenetetrazole-induced epileptic seizures in mice. Int. J. Nanomed. 2020;15:6339–6353. - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

