Autologous tooth bone graft block compared with advanced platelet-rich fibrin in alveolar ridge preservation: A clinico-radiographic study
- PMID: 38434501
- PMCID: PMC10906784
- DOI: 10.4103/jisp.jisp_43_23
Autologous tooth bone graft block compared with advanced platelet-rich fibrin in alveolar ridge preservation: A clinico-radiographic study
Abstract
Objectives: To determine the clinico-radiographic efficiency of partially demineralized dentin matrix block (PDDM block), a mixture of PDDM with advanced-platelet-rich fibrin+ (A-PRF+) and injectable platelet-rich fibrin versus A-PRF+ alone in alveolar socket preservation.
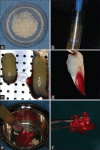
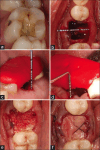
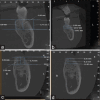
Materials and methods: Sixteen molar teeth indicated for extraction were randomly assigned into two groups. For the test group, sockets were packed with PDDM block and control group, with A-PRF+ plug alone. Clinical and radiographic cone-beam computed tomography methods were used to assess the horizontal and vertical ridge dimensional changes at baseline and 4 months.
Results: Clinically, the mid buccal and palatal crestal height (10.25 ± 0.86 and 9.75 ± 0.28 mm) and alveolar ridge width (11.37 ± 0.25 mm) were significantly higher in the test group as compared to the control group, 4 months after tooth extraction (P < 0.01). Radiographically, there was improved apposition and nonsignificant resorption for the test group in ridge height and width, whereas statistically significant higher resorption was seen in the control group at 4 months.
Conclusion: The application of the PDDM block demonstrated efficacy in maintaining the dimensions of the extraction socket when compared to A-PRF+ alone. This autologous and immune-free regenerative biomaterial is widely obtainable, offering a glimpse into the potential of next-generation biofuels for regeneration.
Keywords: Advanced-platelet-rich fibrin+; alveolar ridge preservation; dentin graft; partially demineralized dentin matrix block.
Copyright: © 2024 Indian Society of Periodontology.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Augmentation of single tooth extraction socket with deficient buccal walls using bovine xenograft with platelet-rich fibrin membrane.BMC Oral Health. 2023 Nov 17;23(1):874. doi: 10.1186/s12903-023-03554-2. BMC Oral Health. 2023. PMID: 37978487 Free PMC article.
-
Alveolar Ridge Preservation Using Autologous Demineralized Tooth Matrix and Platelet-Rich Fibrin Versus Platelet-Rich Fibrin Alone: A Split-Mouth Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial.Implant Dent. 2019 Oct;28(5):455-462. doi: 10.1097/ID.0000000000000918. Implant Dent. 2019. PMID: 31188170 Clinical Trial.
-
Efficacy of Platelet-Rich Fibrin in Preserving Alveolar Ridge Volume and Reducing Postoperative Pain in Site Preservation of Post-Extracted Sockets.Medicina (Kaunas). 2024 Jun 28;60(7):1067. doi: 10.3390/medicina60071067. Medicina (Kaunas). 2024. PMID: 39064496 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Efficacy of platelet-rich fibrin on bone formation, part 1: Alveolar ridge preservation.Int J Oral Implantol (Berl). 2021 May 12;14(2):181-194. Int J Oral Implantol (Berl). 2021. PMID: 34006080
-
Effect of platelet-rich fibrin on alveolar ridge preservation: A systematic review.J Am Dent Assoc. 2019 Sep;150(9):766-778. doi: 10.1016/j.adaj.2019.04.025. J Am Dent Assoc. 2019. PMID: 31439204
Cited by
-
Healing of Extraction Sites after Alveolar Ridge Preservation Using Advanced Platelet-Rich Fibrin: A Retrospective Study.Bioengineering (Basel). 2024 Jun 3;11(6):566. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering11060566. Bioengineering (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38927802 Free PMC article.
-
Progress in Dentin-Derived Bone Graft Materials: A New Xenogeneic Dentin-Derived Material with Retained Organic Component Allows for Broader and Easier Application.Cells. 2024 Oct 31;13(21):1806. doi: 10.3390/cells13211806. Cells. 2024. PMID: 39513913 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tooth Graft and Platelet-Rich Fibrin Mixture for Oral Bone Reconstruction and Preservation: A Scoping Review.Clin Exp Dent Res. 2025 Aug;11(4):e70160. doi: 10.1002/cre2.70160. Clin Exp Dent Res. 2025. PMID: 40741725 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jonasson G, Skoglund I, Rythén M. The rise and fall of the alveolar process: Dependency of teeth and metabolic aspects. Arch Oral Biol. 2018;96:195–200. - PubMed
-
- Tan WL, Wong TL, Wong MC, Lang NP. A systematic review of post-extractional alveolar hard and soft tissue dimensional changes in humans. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2012;23(Suppl 5):1–21. - PubMed
-
- Darby I, Chen S, De Poi R. Ridge preservation: What is it and when should it be considered. Aust Dent J. 2008;53:11–21. - PubMed
-
- Misch CM. Autogenous bone is still the gold standard of graft materials in 2022. J Oral Implantol. 2022;48:169–70. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
