Evaluation and comparison of three-dimensional finite element analysis of stress distribution in immediately placed and loaded conventional and customized three-dimensional printed dental implants
- PMID: 38434503
- PMCID: PMC10906799
- DOI: 10.4103/jisp.jisp_585_22
Evaluation and comparison of three-dimensional finite element analysis of stress distribution in immediately placed and loaded conventional and customized three-dimensional printed dental implants
Abstract
Aim: The aim of this study was to evaluate and compare the stress distribution patterns in immediately placed and loaded conventional and customized three-dimensional (3D) printed dental implants by 3D finite element analysis.
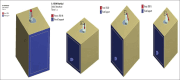
Materials and methods: Twelve 3D finite element models [Group A-3 models; Group B-9 models] with 72 test conditions which were modeled and compared from customized 3D printed dental implants [Group A] and 3 commercially available implant systems [Group B] (Straumann, Ankylos, and Astratech) using "SolidWorks". All models were embedded in extraction socket models of the maxillary central incisor (CI) and Canine (C), Mandibular 1st Premolar. An occlusal loading by axial and nonaxial force of 100 N and 150 N at 30° and 45° was applied on the abutment using the "ANSYS" Suite. Customized 3D printed dental implant (Group A) for maxilla (Max.) CI, Max. C, and mandibular 1st premolar (PM) socket model was compared with three commercial available dental implant systems (Group B) for Max. CI, Max. C, and mandible (Mand.) 1st PM socket model to understand the stress distribution patterns.
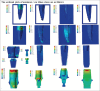
Results: With increasing oblique loads, von Mises stresses were reduced for the customized group as compared to conventional implants. Increased axial loads caused proportionate increase in the stresses for both groups, yet remained under the physiologic limits in all test conditions. Higher stresses were observed in cortical bone than in cancellous bone at bone-implant contact in general. Marked reduction in von Mises stress was observed at the boundary between compact and cancellous bone. Customized 3D printed implants performed better for oblique loads and comparable for axial load stress distribution in comparison to conventional implant systems in Max. CI and C, Mand. 1st PM.
Conclusion: Thus, customized 3D printed implants appear a promising alternative for immediately placed immediately loaded protocols, with additional benefits in specific clinical situations.
Keywords: Customized three-dimensional printed dental implant; dental implant; finite element analysis; immediate implant loading; immediate implant placement.
Copyright: © 2024 Indian Society of Periodontology.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Effect of different restorative crown and customized abutment materials on stress distribution in single implants and peripheral bone: A three-dimensional finite element analysis study.J Prosthet Dent. 2018 Mar;119(3):437-445. doi: 10.1016/j.prosdent.2017.03.008. Epub 2017 Jun 20. J Prosthet Dent. 2018. PMID: 28645667
-
[Three dimensional finite element analysis of biomechanical distribution of dental implants with immediate loading].Hua Xi Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2011 Apr;29(2):121-4. Hua Xi Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2011. PMID: 21598477 Chinese.
-
Design and Biomechanical Analysis of a Customized Angled Abutment Based on Tooth Inclination for Immediate Implant Placement in the Anterior Maxilla.Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2024 Dec 11;39(6):209-216. doi: 10.11607/jomi.10877. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2024. PMID: 38728145
-
Customized 3D-Printed Mesh, Membrane, Bone Substitute, and Dental Implant Applied to Guided Bone Regeneration in Oral Implantology: A Narrative Review.Dent J (Basel). 2024 Sep 25;12(10):303. doi: 10.3390/dj12100303. Dent J (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39452431 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Better models, better treatment? a systematic review of current three dimensional (3D) in vitro models for implant-associated infections.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2025 Apr 25;13:1569211. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2025.1569211. eCollection 2025. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2025. PMID: 40352353 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adell R, Lekholm U, Rockler B, Brånemark PI. A 15-year study of osseointegrated implants in the treatment of the edentulous jaw. Int J Oral Surg. 1981;10:387–416. - PubMed
-
- Adell R, Eriksson B, Lekholm U, Brånemark PI, Jemt T. Long-term follow-up study of osseointegrated implants in the treatment of totally edentulous jaws. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 1990;5:347–59. - PubMed
-
- Albrektsson T. A multicenter report on osseointegrated oral implants. J Prosthet Dent. 1988;60:75–84. - PubMed
-
- Anderson TR, Slotkin TA. Maturation of the adrenal medulla –IV. Effects of morphine. Biochem Pharmacol. 1975;24:1469–74. - PubMed
-
- Chen ST, Wilson TG, Jr, Hämmerle CH. Immediate or early placement of implants following tooth extraction: Review of biologic basis, clinical procedures, and outcomes. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2004;19(Suppl):12–25. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
