Monitoring of the right ventricular responses to pressure overload: prognostic value and usefulness of echocardiography for clinical decision-making
- PMID: 38434557
- PMCID: PMC10904302
- DOI: 10.21037/cdt-23-380
Monitoring of the right ventricular responses to pressure overload: prognostic value and usefulness of echocardiography for clinical decision-making
Abstract
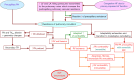
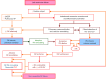
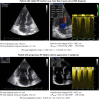
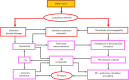
Regardless of whether pulmonary hypertension (PH) results from increased pulmonary venous pressure in left-sided heart diseases or from vascular remodeling and/or obstructions in pre-capillary pulmonary vessels, overload-induced right ventricular (RV) dysfunction and its final transition into right-sided heart failure is a major cause of death in PH patients. Being particularly suited for non-invasive monitoring of the right-sided heart, echocardiography has become a useful tool for optimizing the therapeutic decision-making and evaluation of therapy results in PH. The review provides an updated overview on the pathophysiological insights of heart-lung interactions in PH of different etiology, as well as on the diagnostic and prognostic value of echocardiography for monitoring RV responses to pressure overload. The article focuses particularly on the usefulness of echocardiography for predicting life-threatening aggravation of RV dysfunction in transplant candidates with precapillary PH, as well as for preoperative prediction of post-operative RV failure in patients with primary end-stage left ventricular (LV) failure necessitating heart transplantation or a LV assist device implantation. In transplant candidates with refractory pulmonary arterial hypertension, a timely prediction of impending RV decompensation can contribute to reduce both the mortality risk on the transplant list and the early post-transplant complications caused by severe RV dysfunction, and also to avoid combined heart-lung transplantation. The review also focuses on the usefulness of echocardiography for monitoring the right-sided heart in patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome, particularly in those with refractory respiratory failure requiring extracorporeal membrane oxygenation support. Given the pathophysiologic particularity of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) infection to be associated with a high incidence of thrombotic microangiopathy-induced increase in the pulmonary resistance, echocardiography can improve the selection of temporary mechanical cardio-respiratory support strategies and can therefore contribute to the reduction of mortality rates. On the whole, the review aims to provide a theoretical and practical basis for those who are or intend in the future to be engaged in this highly demanding field.
Keywords: Echocardiography; pulmonary hypertension (PH); right heart failure (RHF); right ventricle; right ventricle-pulmonary arterial uncoupling (RV-PA uncoupling).
2024 Cardiovascular Diagnosis and Therapy. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: The author has completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://cdt.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/cdt-23-380/coif). The author has no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Heart-lung interactions in COVID-19: prognostic impact and usefulness of bedside echocardiography for monitoring of the right ventricle involvement.Heart Fail Rev. 2022 Jul;27(4):1325-1339. doi: 10.1007/s10741-021-10108-7. Epub 2021 Apr 17. Heart Fail Rev. 2022. PMID: 33864580 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Echocardiographic assessment of the right ventricle: Impact of the distinctly load dependency of its size, geometry and performance.Int J Cardiol. 2016 Oct 15;221:1132-42. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2016.07.014. Epub 2016 Jul 7. Int J Cardiol. 2016. PMID: 27474972 Review.
-
Pulmonary vascular mechanical consequences of ischemic heart failure and implications for right ventricular function.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2019 May 1;316(5):H1167-H1177. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00319.2018. Epub 2019 Feb 15. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30767670 Free PMC article.
-
Right ventricle dilation as a prognostic factor in refractory acute respiratory distress syndrome requiring veno-venous extracorporeal membrane oxygenation.Minerva Anestesiol. 2016 Oct;82(10):1043-1049. Epub 2016 Mar 8. Minerva Anestesiol. 2016. PMID: 26957118
-
Clinical Determinants and Prognostic Implications of Right Ventricular Dysfunction in Pulmonary Hypertension Caused by Chronic Lung Disease.J Am Heart Assoc. 2019 Jan 22;8(2):e011464. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.118.011464. J Am Heart Assoc. 2019. PMID: 30646788 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Right ventricular mechanical support as a bridge to lung transplantation: A literature review of current practices.JHLT Open. 2025 Jun 15;9:100316. doi: 10.1016/j.jhlto.2025.100316. eCollection 2025 Aug. JHLT Open. 2025. PMID: 40735633 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rebuttal to the letter "Assessment of COVID-19-related right ventricular morphological and functional alterations and evaluation of their impact on the course of the disease".Ann Intensive Care. 2024 Apr 24;14(1):63. doi: 10.1186/s13613-024-01292-4. Ann Intensive Care. 2024. PMID: 38656464 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Improving the Prioritization of Heart Transplantation Candidates for Optimal Clinical Outcomes: A Narrative Review.Curr Cardiol Rep. 2025 Jan 8;27(1):8. doi: 10.1007/s11886-024-02150-2. Curr Cardiol Rep. 2025. PMID: 39777580 Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
