M3 subtype of muscarinic acetylcholine receptor inhibits cardiac fibrosis via targeting microRNA-29b/beta-site app cleaving enzyme 1 axis
- PMID: 38434562
- PMCID: PMC10904290
- DOI: 10.21037/cdt-23-309
M3 subtype of muscarinic acetylcholine receptor inhibits cardiac fibrosis via targeting microRNA-29b/beta-site app cleaving enzyme 1 axis
Abstract
Background: Previous studies have confirmed that choline exerts anti-fibrotic effect in the heart by activating the M3 subtype of muscarinic acetylcholine receptor (M3 receptor), but the mechanism remains to be clarified. MicroRNA-29b (miR-29b) plays an important role in the fibrotic process and can directly target collagen to resist myocardial fibrosis. This study investigated whether miR-29b is involved in the anti-fibrotic effect of activating M3 receptor.
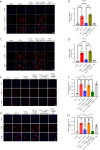
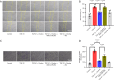
Methods: Proliferation of cardiac fibroblasts was induced by transforming growth factor (TGF)-β1 in vitro. The expression of miR-29b in cardiac fibroblasts was detected by quantitative real-time reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR). Protein levels of collagens I, connective tissue growth factor (CTGF), α-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA) and beta-site app cleaving enzyme 1 (BACE1) were determined by Western blot analysis. Fibroblast-myofibroblast transition was identified by immunofluorescence staining. Proliferation and migration of cardiac fibroblasts as indicated by transwell and scratch assays.
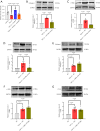
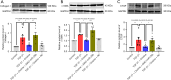
Results: The expression of miR-29b decreased when treated with TGF-β1 (P=0.0389) and increased after choline stimulated (P=0.0001). Overexpression of miR-29b could reverse the high expression of collagen I (P<0.0001), α-SMA (P=0.0007), and CTGF (P=0.0038) induced by TGF-β1, whereas inhibition of miR-29b had a tendency to even further increase the expression of fibrosis markers. Meanwhile, inhibition of miR-29b could reverse the anti-fibrotic effect of choline, increasing the expression of collagen I (P=0.0040), α-SMA (P=0.0001), and CTGF (P=0.0185), and promoting the fibroblast proliferation and migration. Moreover, BACE1 protein level, increased after TGF-β1 treatment (P=0.0037) and reversed by overexpression of miR-29b (P=0.0493). Choline could reduce the increase of BACE1 induced by TGF-β1 (P=0.0264), and 4-diphenylacetoxy-N-methyl-piperidine methiodide (4-DAMP) increased the expression of BACE1 (P=0.0060). Furthermore, overexpression of BACE1 could reverse the protective effect of miR-29b in cardiac fibrosis, increasing the protein level of collagen I (P=0.0404).
Conclusions: The results suggested that M3 receptor activation could exert cardioprotective effects in cardiac fibrosis by mediating miR-29b/BACE1 axis.
Keywords: Cardiac fibrosis; M3 subtype of muscarinic acetylcholine receptor (M3 receptor); beta-site app cleaving enzyme 1 (BACE1); microRNA-29b (miR-29b).
2024 Cardiovascular Diagnosis and Therapy. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://cdt.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/cdt-23-309/coif). All authors report that this work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China. The authors have no other conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
MicroRNA-223 Regulates Cardiac Fibrosis After Myocardial Infarction by Targeting RASA1.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;46(4):1439-1454. doi: 10.1159/000489185. Epub 2018 Apr 19. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018. PMID: 29689569
-
Cyclosporine A promotes cell proliferation, collagen and α-smooth muscle actin expressions in rat gingival fibroblasts by Smad3 activation and miR-29b suppression.J Periodontal Res. 2016 Dec;51(6):735-747. doi: 10.1111/jre.12350. Epub 2016 Jan 6. J Periodontal Res. 2016. PMID: 26738448
-
Choline Attenuates Cardiac Fibrosis by Inhibiting p38MAPK Signaling Possibly by Acting on M3 Muscarinic Acetylcholine Receptor.Front Pharmacol. 2019 Nov 21;10:1386. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2019.01386. eCollection 2019. Front Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31849653 Free PMC article.
-
Downregulation of microRNA-29b in cancer and fibrosis: molecular insights and clinical implications.Drug Discov Today. 2024 Nov;29(11):104190. doi: 10.1016/j.drudis.2024.104190. Epub 2024 Sep 24. Drug Discov Today. 2024. PMID: 39322175 Review.
-
Potential molecular mechanism underlying cardiac fibrosis in diabetes mellitus: a narrative review.Egypt Heart J. 2023 Jun 12;75(1):46. doi: 10.1186/s43044-023-00376-z. Egypt Heart J. 2023. PMID: 37306727 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The value of miRNA-29b in the diagnosis of myocardial infarction and the evaluation of cardiac function after myocardial infarction.Cardiovasc Diagn Ther. 2025 Jun 30;15(3):539-549. doi: 10.21037/cdt-24-561. Epub 2025 Jun 25. Cardiovasc Diagn Ther. 2025. PMID: 40656787 Free PMC article.
-
Research progress in myocardial function and diseases related to muscarinic acetylcholine receptor (Review).Int J Mol Med. 2025 Jun;55(6):86. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2025.5527. Epub 2025 Apr 4. Int J Mol Med. 2025. PMID: 40183403 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mini Review: the non-neuronal cardiac cholinergic system in type-2 diabetes mellitus.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2024 Sep 2;11:1425534. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2024.1425534. eCollection 2024. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2024. PMID: 39314774 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
