The biological interplay between air pollutants and miRNAs regulation in cancer
- PMID: 38434617
- PMCID: PMC10905188
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2024.1343385
The biological interplay between air pollutants and miRNAs regulation in cancer
Abstract
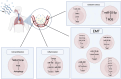
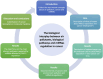
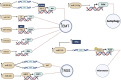
Air pollution, especially fine particulate matter (PM2.5, with an aerodynamic diameter of less than 2.5 μm), represents a risk factor for human health. Many studies, regarding cancer onset and progression, correlated with the short and/or long exposition to PM2.5. This is mainly mediated by the ability of PM2.5 to reach the pulmonary alveoli by penetrating into the blood circulation. This review recapitulates the methodologies used to study PM2.5 in cellular models and the downstream effects on the main molecular pathways implicated in cancer. We report a set of data from the literature, that describe the involvement of miRNAs or long noncoding RNAs on the main biological processes involved in oxidative stress, inflammation, autophagy (PI3K), cell proliferation (NFkB, STAT3), and EMT (Notch, AKT, Wnt/β-catenin) pathways. microRNAs, as well as gene expression profile, responds to air pollution environment modulating some key genes involved in epigenetic modification or in key mediators of the biological processes described below. In this review, we provide some scientific evidences about the thigh correlation between miRNAs dysregulation, PM2.5 exposition, and gene pathways involved in cancer progression.
Keywords: PM2.5; lung; microRNAs (miRNAs); particulate matter; pollution.
Copyright © 2024 Giammona, Remedia, Porro, Lo Dico and Bertoli.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Beelen R., Hoek G., Raaschou-Nielsen O., Stafoggia M., Andersen Z. J., Weinmayr G., et al. (2015). Natural-cause mortality and long-term exposure to particle components: an analysis of 19 European cohorts within the multi-center ESCAPE Project. Environ. Health Perspect. 123, 525–533. 10.1289/ehp.1408095 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

