Social influence and external feedback control in humans
- PMID: 38434659
- PMCID: PMC10905169
- DOI: 10.12688/f1000research.133295.3
Social influence and external feedback control in humans
Abstract
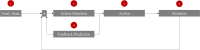
This article aims to unravel the dynamics of social influence by examining the processes that occur when one person is the target of another's influence. We hypothesized that these processes are part of a feedback loop system in an individual. This loop involves the situation (input), a goal state (reference), a comparator, a selection mechanism, a feedback predictor, and an action (output). Each element can become the target of social influence, and different types of social influence can be classified and explained by how these elements are targeted. For instance, attempting to persuade another person with strong arguments targets the goal state of the affected individual, while obedience targets the selection mechanism, and violence targets the action. In summary, this article aims to categorize, order, and explain phenomena in social influence research using a feedback loop framework focusing on the influenced individual.
Keywords: feedback control; social influence; social interaction.
Copyright: © 2024 Weiß M et al.
Conflict of interest statement
No competing interests were disclosed.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Social is special: A normative framework for teaching with and learning from evaluative feedback.Cognition. 2017 Oct;167:91-106. doi: 10.1016/j.cognition.2017.03.006. Epub 2017 Mar 22. Cognition. 2017. PMID: 28341268
-
Depicting "the system": How structural racism and disenfranchisement in the United States can cause dynamics in community violence among males in urban black communities.Soc Sci Med. 2021 Mar;272:113469. doi: 10.1016/j.socscimed.2020.113469. Epub 2020 Nov 7. Soc Sci Med. 2021. PMID: 33601249
-
To run with the herd or not: Electrophysiological dynamics are associated with preference change in crowdfunding.Neuropsychologia. 2019 Nov;134:107232. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2019.107232. Epub 2019 Oct 15. Neuropsychologia. 2019. PMID: 31626829
-
Violence and serotonin: influence of impulse control, affect regulation, and social functioning.J Neuropsychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2003 Summer;15(3):294-305. doi: 10.1176/jnp.15.3.294. J Neuropsychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2003. PMID: 12928505 Review.
-
Social contagion, violence, and suicide among adolescents.Curr Opin Psychiatry. 2023 May 1;36(3):237-242. doi: 10.1097/YCO.0000000000000858. Epub 2023 Feb 15. Curr Opin Psychiatry. 2023. PMID: 36762666 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The amygdala and the pursuit of future rewards.Front Neurosci. 2025 Jan 22;18:1517231. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2024.1517231. eCollection 2024. Front Neurosci. 2025. PMID: 39911407 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Need for affect, need for cognition, and the desire for independence.PLoS One. 2023 Feb 9;18(2):e0280457. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0280457. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 36757914 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aaker JL, Lee AY: “I” seek pleasures and “we” avoid pains: The role of self-regulatory goals in information processing and persuasion. J. Consum. Res. 2001;28(1):33–49. 10.1086/321946 - DOI
-
- Aiello A, Tesi A, Pratto F, et al. : Social dominance and interpersonal power: Asymmetrical relationships within hierarchy-enhancing and hierarchy-attenuating work environments. J. Appl. Soc. Psychol. 2018;48(1):35–45. 10.1111/jasp.12488 - DOI
-
- Asch SE: Studies in the principles of judgments and attitudes: II. Determination of judgments by group and by ego standards. J. Soc. Psychol. 1940;12(2):433–465. 10.1080/00224545.1940.9921487 - DOI
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources