Case Report: Remote magnetic navigation and accessory pathways ablation in a single ventricle young adult with complex corrective surgeries
- PMID: 38434729
- PMCID: PMC10904613
- DOI: 10.3389/fped.2024.1358505
Case Report: Remote magnetic navigation and accessory pathways ablation in a single ventricle young adult with complex corrective surgeries
Abstract
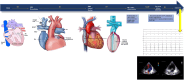
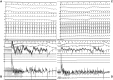
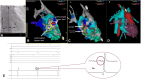
Supraventricular arrhythmias have become an increasingly significant contributor to the risk of mortality and morbidity in adults with complex congenital heart disease (CHD), especially in light of recent advances in palliative corrective surgeries. Because of their unique characteristics, they demand specific treatment approaches. While pharmaco-logical interventions are an option, they have limited effectiveness and may lead to side effects. Although performing radiofrequency ablation (RFA) can be exceptionally challenging in patients with complex CHD, due to particular vascular access and also modified anatomy, it has paved the way to enhance comprehension of the underlying mechanisms of supraventricular arrhythmias. This, in turn, enables the provision of improved therapies and, ultimately, an enhancement in the quality of life and symptom management for these patients. The purpose of this case report is to highlight the benefits of utilizing advanced technologies such as three-dimensional electro-anatomical mapping systems, remote magnetic navigation, and highly flexible mapping and ablation catheters during RFA in a young adult with complex congenital heart disease. Although he lacked venous connections to the right atrium (RA) due to multiple corrective surgeries we, remarkably, were capable to advance a decapolar deflectable diagnostic catheter inside the Fontan tunnel and from there to record and stimulate the RA. Successful ablation of two accessory pathways was achieved with no arrhythmia recurrence during follow-up.
Keywords: accessory pathways; atrioventricular reentrant tachycardia; case report; congenital heart disease; electroanatomic mapping; remote magnetic navigation; surgical correction procedures.
© 2024 Paja, Gondoș, Deaconu, Cinteză and Vătășescu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Advanced electrophysiologic mapping systems: an evidence-based analysis.Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2006;6(8):1-101. Epub 2006 Mar 1. Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2006. PMID: 23074499 Free PMC article.
-
Successful Radiofrequency Ablation of Recurrent Supraventricular Tachycardia in a Patient with Complex Congenital Heart Disease.Am J Case Rep. 2020 Dec 2;21:e928147. doi: 10.12659/AJCR.928147. Am J Case Rep. 2020. PMID: 33262322 Free PMC article.
-
Catheter Ablation of Atrial Arrhythmias in Patients Post-Fontan.Can J Cardiol. 2022 Jul;38(7):1036-1047. doi: 10.1016/j.cjca.2022.02.023. Epub 2022 Mar 1. Can J Cardiol. 2022. PMID: 35240252 Review.
-
Remote magnetic navigation shows superior long-term outcomes in pediatric atrioventricular (nodal) tachycardia ablation compared to manual radiofrequency and cryoablation.Int J Cardiol Heart Vasc. 2021 Oct 1;37:100881. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcha.2021.100881. eCollection 2021 Dec. Int J Cardiol Heart Vasc. 2021. PMID: 34646933 Free PMC article.
-
Ablation of supraventricular arrhythmias in adult congenital heart disease: A contemporary review.Arch Cardiovasc Dis. 2017 May;110(5):334-345. doi: 10.1016/j.acvd.2017.01.007. Epub 2017 Mar 27. Arch Cardiovasc Dis. 2017. PMID: 28359691 Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

